How are synthetic alkynes used to treat Parkinson’s disease?
1 Answer
Feb 11, 2017
They inhibit the enzyme that oxidizes dopamine in the brain.
Explanation:
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays an important role in movement and balance.
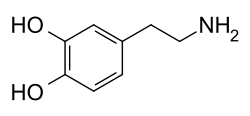
When the brain cannot produce enough dopamine, Parkinson's disease results.
Dopamine is oxidized by an enzyme called monoamine oxidase.
Various drugs containing alkyne groups have been developed to inhibit this enzyme.
Among them are tremorine

and rasagiline.

They appear to form covalent bonds to the active site of the enzyme.
Since dopamine cannot bind, it can no longer be oxidized.
Patients on these drugs must still take their regular medications, but they can do so at longer intervals.

