Question #8711a
1 Answer
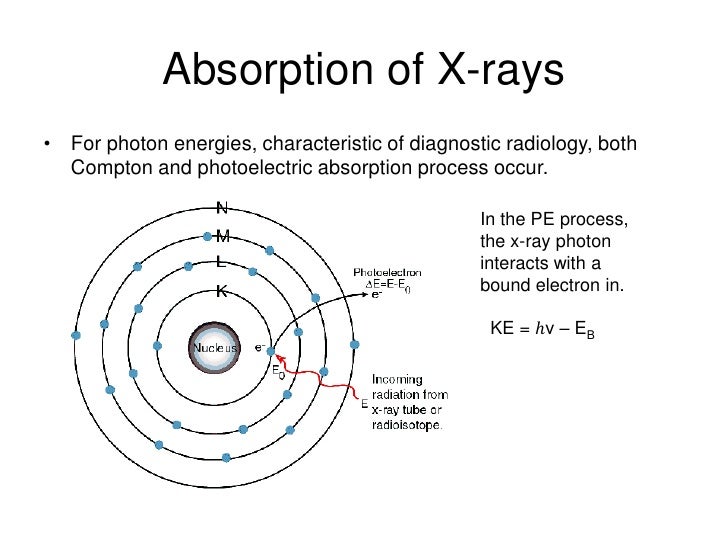
This question is an example of the photoelectric effect
Photoelectric Effect
When a photon of sufficient energy hits the surface of an object electron are released depending on the energy of the photon.Less electrons are emitted when the object is hit by a photon of less energy and vice versa.
The stopping potential is the potential energy measured in volts (joules/coulomb) that must be applied to stop the electrons from being ejected from the surface when the light is shone on it.
This will make the KE of the electron 0.
Plug in the variables
4.065625eV is the work function of cadium

