Why are certain epoxides dangerous?
1 Answer
Epoxides are carcinogenic because they disrupt our DNA.
Explanation:
Epoxides are three-membered cyclic ethers.
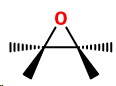
They are highly strained because the nominal bond angles are 60° instead of 109.5°.
They tend to react with other molecules to open the ring and reduce the strain.
A common pro-carcinogen is benzo[a]pyrene.
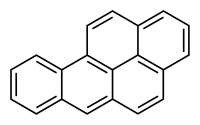
It is a constituent of automobile exhaust, smog, cigarette smoke and charcoal-cooked foods.
When the body absorbs benzo[a]pyrene, it tries to make it water-soluble so it can be excreted in the urine or feces.
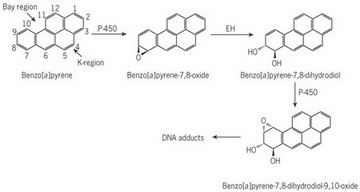
(From researcgate.net)
It converts the benzo[a]pyrene into benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-epoxide.
This is hydrolyzed to the 7,8-dihydrodiol, which is further converted into benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide.
Once formed, the epoxide can π stack with the bases in DNA where the epoxide group reacts with guanine residues.

This distorts the structure of DNA and causes errors in DNA replication.
If these mutations occur in a gene that encodes a molecule that regulates the production of cells, the result may be cancer.

