How do you use Riemann sums to evaluate the area under the curve of f(x) = 4 sin xf(x)=4sinx on the closed interval [0, 3pi/2], with n=6 rectangles using right endpoints?
2 Answers
Use your calculator.
Explanation:
R RS = 1.355 RRS=1.355
Explanation:
We have:
f(x) = 4sinx f(x)=4sinx
We want to calculate over the interval
Deltax = ((3pi)/2-0)/6 = (3pi)/12
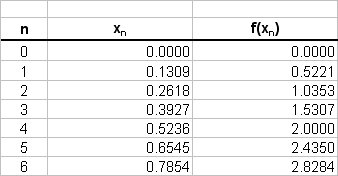
Note that we have a fixed interval (strictly speaking a Riemann sum can have a varying sized partition width). The values of the function are tabulated as follows;
Right Riemann Sum
R RS = sum_(r=1)^4 f(x_i)Deltax_i
" " = 0.1309 * (0.5221 + 1.0353 + 1.5307 + 2 + 2.435 + 2.8284)
" " = 0.1309 * (10.3516)
" " = 1.355
Actual Value
For comparison of accuracy:
Area = int_0^((3pi)/12) \ 4sinx \ dx
" " = [-4cosx]_0^((3pi)/12)
" " = -4[cosx]_0^((3pi)/12)
" " = -4(cos ((3pi)/12)-cos0)
" " = -4(sqrt(2)/2-1)
" " = 1.1715