Question #e6fe4
1 Answer
Should stand around
Explanation:
This can be solved using kinematics.
We have the following information:
#|-> v=4.5"m"//"s"# #|->theta=25^o# #|->h_i=12"m"# #|->h_f~~0"m"# #|->a=-g=-9.8"m"//"s"^2#
We will have to decompose the velocity vector into its parallel (x, horizontal) and perpendicular (y, vertical) components, and use multiple kinematic equations to solve for the displacement.
Diagram:
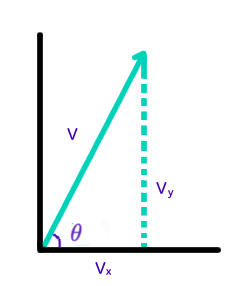
We can use trigonometry to find the components of the initial velocity vector.
#sin(theta)="opposite"/"hypotenuse"#
#=>sin(theta)=v_y/v#
#=>v_y=vsin(theta)#
#=>v_y=4.5sin(25^o)#
#=>color(darkblue)(v_y=1.902"m"//"s")#
Similarly, we find that
We can use the perpendicular component of velocity to calculate the flight time of the beanbag, knowing that for an object in free fall,
#h_f-h_i=v_(iy)Deltat+1/2a(Deltat)^2#
We want to solve for
#t=(-b+-sqrt(b^2-4ac))/(2a)#
#=>t=(-1.9+-sqrt((1.9)^2-4(-4.9)(12)))/(-9.8)#
#=>color(darkblue)(t~~1.77"s")#
Using the flight time, we can now calculate the range of the projectile using the following kinematic:
#Deltax=v_(ix)Deltat+1/2a(Deltat)^2#
We want to solve for
Because there is no horizontal acceleration for an object in free fall:
#Deltax=v_(ix)Deltat#
#=>=(4.078"m"//"s")(1.77"s")#
#=>=07.221"m"#
#=>~~7.2"m"# .

