How does equivalent conductance vary with concentration?
1 Answer
Equivalent conductance increases as concentration decreases.
Explanation:
The specific conductance (
A more fundamental unit is the equivalent conductance
You can think of
The formula for equivalent conductance is
#color(blue)(bar(ul(|color(white)(a/a)Λ = kappa × 1000/Ncolor(white)(a/a)|)))" "#
where
For strong electrolytes, the number of ions does not change with dilution because strong electrolytes are already completely ionized.
However, in concentrated solutions of strong electrolytes, the ions are so close together that they tend to group themselves into solvated ion pairs.
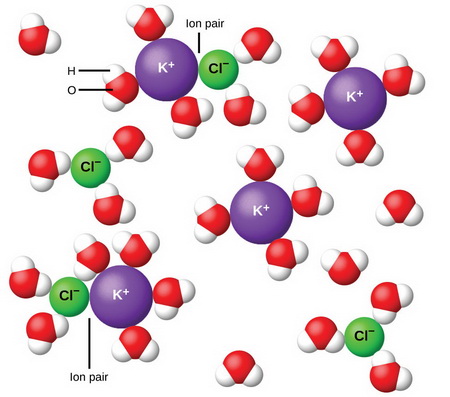
(From BC Open Textbooks)
The formation of these ion pairs reduces the conducting ability of the ions.
With dilution, the ions become far apart from one another and ion pair formation decreases.
As a result, equivalent conductivity increases with dilution.
The equivalent conductance of weak electrolytes also increases with dilution, but the effect is not linear because number of ions increases with dilution.

