What happens during the Calvin-Benson cycle, or dark reaction?
1 Answer
In Calvin cycle or dark reaction, sugars are formed by using the chemical energy of
Explanation:
Equation for dark reaction:
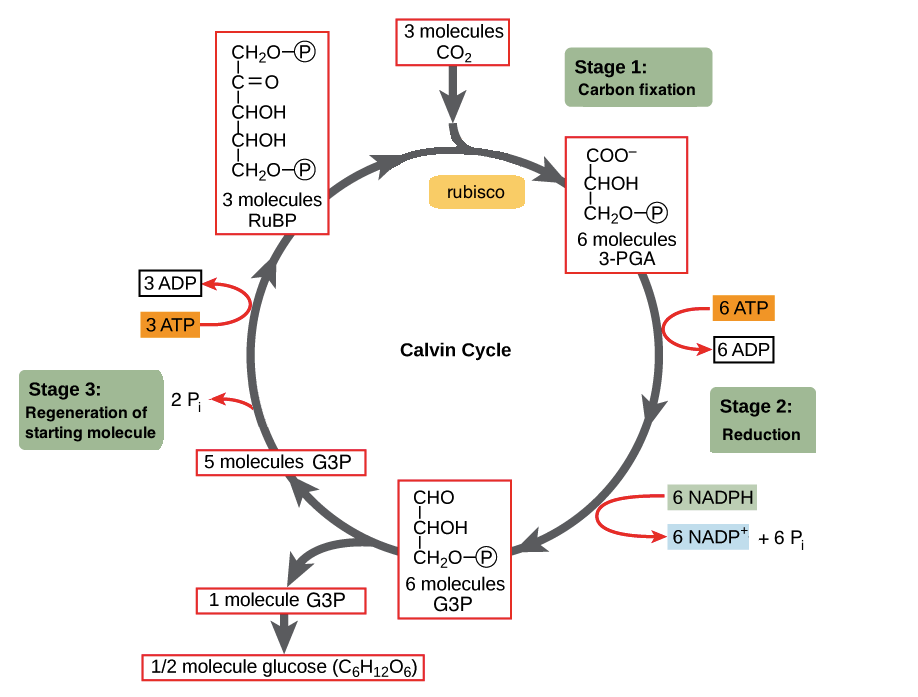
Diagram of Calvin cycle:
Steps in Calvin Cycle:
1st step: Carbon fixation:
It refers to the initial incorporation of
Because;
-
Calvin cycle begins by the reaction of CO2 with highly reactive phosphorylated five carbon-sugar named ribulose bisphosphate(RuBP).
-
This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase also known as Rubisco .
- The product of this reaction is highly unstable six-carbon intermediate that immediately breaks into two molecules of three-carbon-compound named 3-phosphoglycerate(PGA).
- The carbon that was originally a part of
#CO_2# molecule is now a part of an organic compound which means carbon has been fixed .
2nd step: Reduction:
In this step, fixed carbon is reduced to energy rich G3P with the energy and reducing power of ATP and NADPH respectively.
-
Each molecule of PGA recieves an additional phosphate from ATP of light reaction and form 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
-
It is reduced to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate(G3P) by recieving a pair of electrons donated from NADPH of light reactions.
Actually G3P is the carbohydrate that is produced directly from Calvin cycle. -
For every
#3# molecules of#CO_2# entering the cycle and combining with#3# molecules of RuBp,#6# molecules of G3P are produced. But only#1# molecule of G3P can be counted as a net gain of carbohydrate.
Because out of every#6# molecules of G3P formed, only one molecule leaves the cycle to be used by plants for making glucose and other carbohydrates; the other five molecules are recycled to regenerate the three molecules of five carbon RuBP, the#CO_2# acceptor.
3rd step: Regeneration of
-
Through a complex series of reactions, the carbon skeletons of five molecules of three-carbon G3P are rearranged into three molecules of five-carbon ribulose phosphate(RuP).
-
Each RuP is phosphorylated to RuBP. Again
#3# molecules of ATP of light reactions are used for this phosphorylation of#3#
RuP. -
These RuBP are now prepared to recieve
#CO_2# again, and the cycle continues.