Question #653d6
1 Answer
See below.
Explanation:
First, we need to write a balanced chemical reaction for the combustion of ethene:
Now that we have the balanced reaction, we need to draw the Lewis structures of each molecule (which are included below)
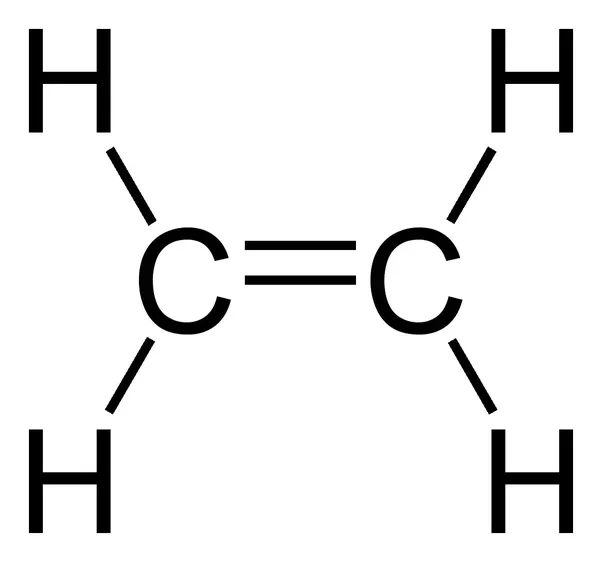
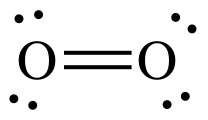
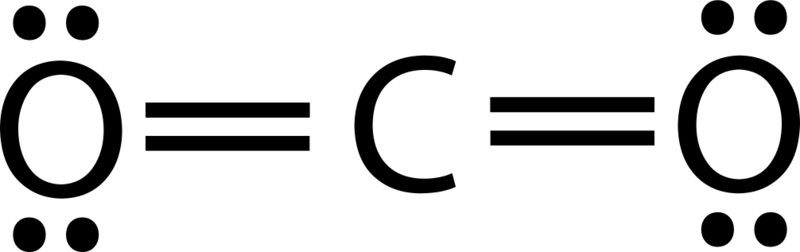
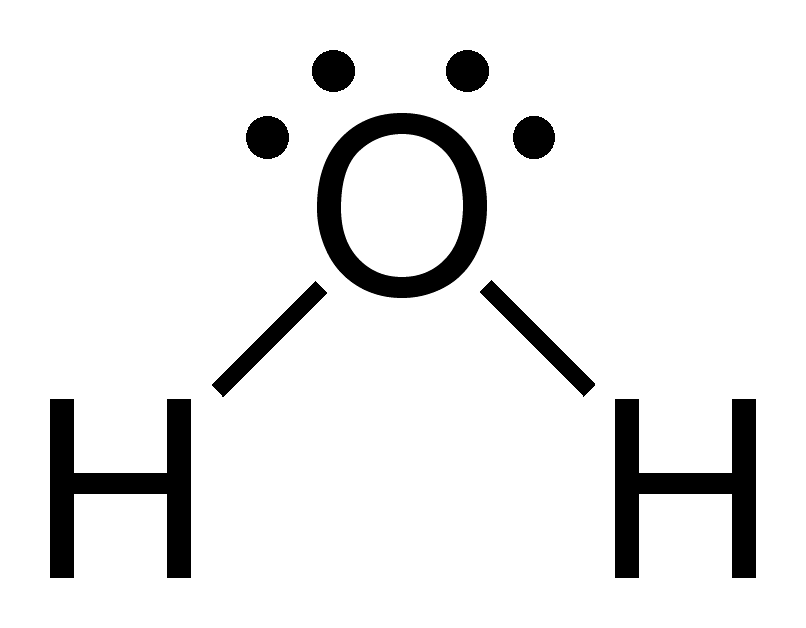
Using the Lewis structures, we can count the number of bonds in each molecule:
There is 1 C=C bond in ethene and 4 C-H bonds.
There is 1 O=O bond in
There are 2 C=O bonds in
Lastly, there are 2 O-H bonds in
Now, we can use this formula in order to calculate
The reason why the bond energies of the products is negative is because on the reactant side of the chemical equation we are breaking bonds (requiring energy) and on the product side of the chemical equation we are forming bonds (releasing energy).
If we plug the values we have in our formula we get this:
**NOTE: for some reason with the bond energy data provided, we end up with an endothermic reaction for the combustion of ethene. This is incorrect, as it should be an exothermic reaction. The formula is correct, so if you could find the correct data for bond energies the same process can be followed to get the right answer.

