Question #610bc
1 Answer
Sexual=a lot of diversity. Asexual=little/no diversity.
Explanation:
In sexual reproduction, 2 parents share 50% of their DNA with each other and effectively produce offspring with a genome that is 50% the father's and 50% the mother's.
Multiple ways genetic diversity can result from sexual reproduction is in crossing over (stage in meiosis where homologous pairs of chromosomes exchange information with each other), independent assortment (where sister chromatids from chromosomes have different possibilities of ending up in certain gametes), and random fertilization (where only 1 male gamete out of many can fertilize a female gamete, both of which have independent assortments of sister chromatids). Here are pictures of those processes:
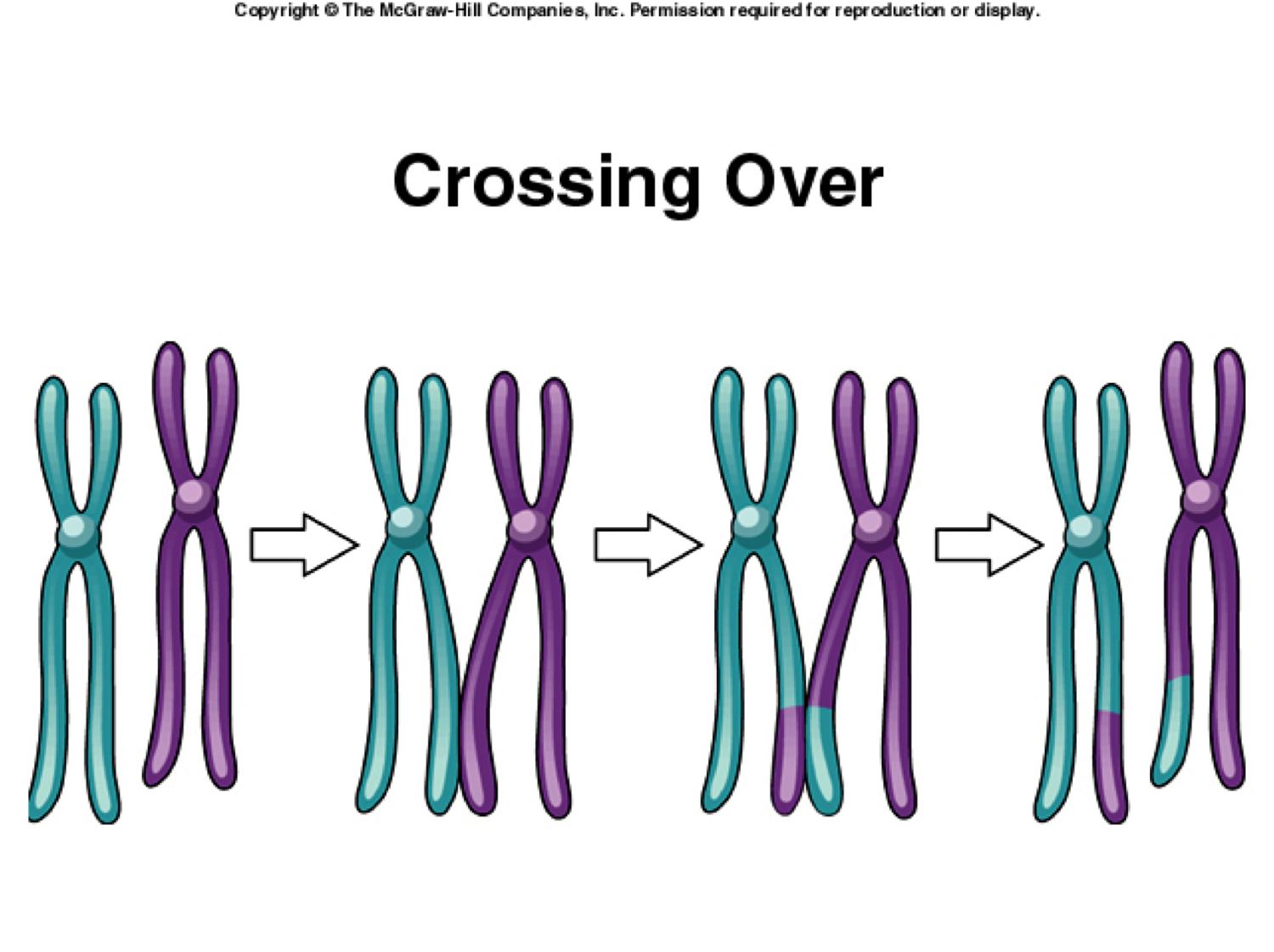 https://www.studyblue.com/notes/note/n/summer-2-2-mitosis-meiosis/deck/6980527
https://www.studyblue.com/notes/note/n/summer-2-2-mitosis-meiosis/deck/6980527
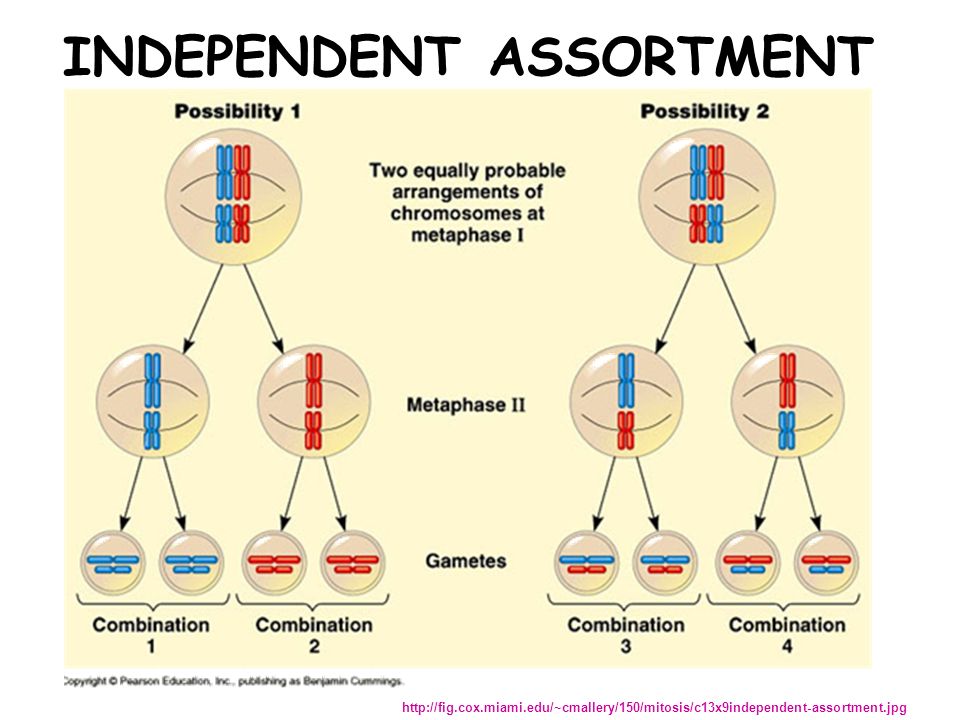 http://slideplayer.com/slide/9347361/
http://slideplayer.com/slide/9347361/
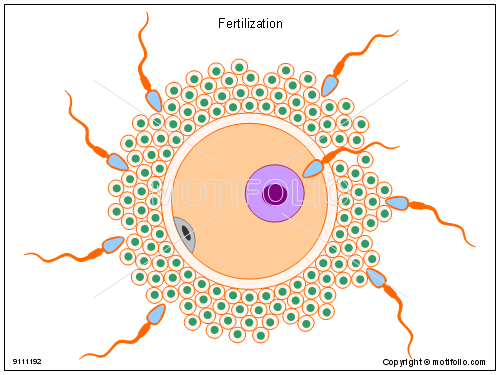 http://lookfordiagnosis.com/mesh_info.php?term=fertilization&lang=1
http://lookfordiagnosis.com/mesh_info.php?term=fertilization&lang=1
*Each sperm cell in this image contains a different assortment of sister chromatids.
Now, for the asexual reproduction part.
In asexual reproduction, the organism is essentially cloning itself. That being said, its offspring will thus be genetic clones of the parent (no diversity).
However, mutations can occur which are the leading cause for genetic diversity in asexual reproduction.

