Question #417b3
1 Answer
Warning! Long Answer!
Explanation:
To start, we need to understand what hardness is.
Scientifically, When water has any of the cations like
The reason it is called hard because the cations undergo a displacement reaction to replace the
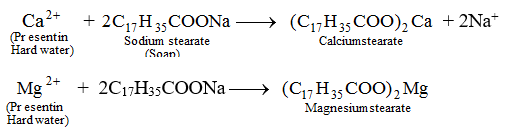
So, to make the water soft again, we need to go through some processes.
The Ion Exchange method is the most efficient of all other methods of Hardness removal. [It can remove both temporary and permanent hardness]
In the Ion Exchange method,
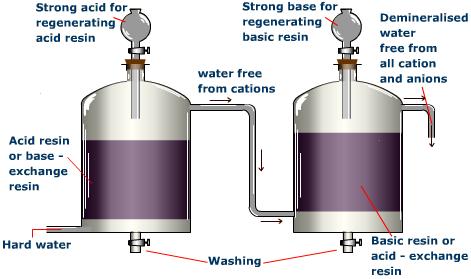
i) First the hard water is passed through the first resin, Cation Exchange Resin or Base - Exchange Resin. This resin is nothing
but a big organic molecule falling in the group of carboxylic acids or sulphonic acids. (
ii) Cation free water goes out and enters the second resin chamber, Anion Exchange Resin or Acid - Exchange Resin This resin is also a big organic molecule falling in the group of Amines(
iii) The water coming out of this chamber is deionized, not distilled. Even it contains nearly zero ions, it still contains germs and other organic materials.
To know how the Resins are regenarted, click here.
Hope this helps.

