Question #536d0
1 Answer
Jan 11, 2018
Explanation:
Nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides(monomers). Nucleotides can be either ribonucleotides
Structure of deoxyribonucleotide
Each deoxyribonucleotide comprises three components:
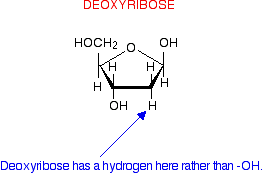
- Deoxyribose sugar :
#"DNA"# contains a five carbon sugar or pentose sugar which lack an oxygen atom because of replacement of hydroxyl group#(OH)# with hydrogen atom#(H)# . That's why called as#color(red)"doeoxy"# ribose sugar.
- Phosphate group:
Phophate group#(PO4^(3-))# of one deoxyribonucleotide interact with deoxyribose sugar of another deoxyribonucleotide forming a phosphodiester bond b/w them. So these help to maintain structure of#"DNA"# and to help the deoxyribonucleotide subunits to make longer stands of#"DNA"# double helix.
The phosphate groups together with doexyribose sugars form backbone of
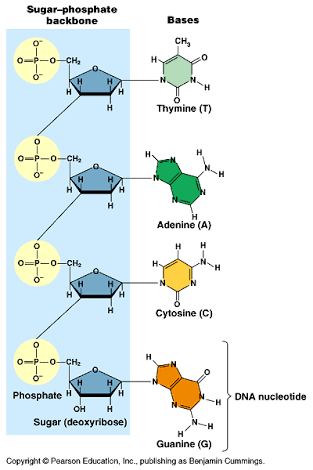
- Nitrogenous bases:
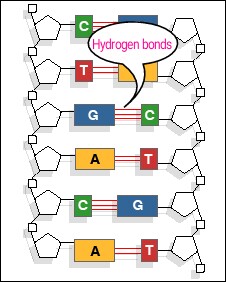
#"DNA"# contains four nitrogenous bases i.e adenine & guanine(purines) and cytosine & thymine(pyrimidines). These bases are linked by hydrogen bonds and are salient in maintaining helical structure of#"DNA"# molecule.
Guanine#(G)# form#3# hydrogen bonds with cytosine#(C)# .
Adenine#(A)# form#2# hydrogen bonds with thymine#(T)# .
Thus overall structure of single deoxyribonucleotide unit can be expressed as:
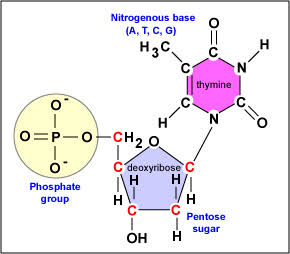
Hope it helps...

