How can I evaluate this integral? (e^3x - 6/2x+1)dx
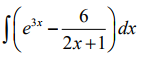
2 Answers
The answer is:
See the steps below...
Explanation:
Apply the sum of integral rule,
Solve each integral separately as:
Substitute
Take the constant out:
Use the integral rule
Substitute back
Solve the other integral:
Substitute
So that after taking the constant out we get:
Apply the common integral rule
By substituting back
So after adding the constant, the solution becomes:
Recall the Rule that,
It can be very easily proved by using the subst. for
In this accordance, we have,
Finally,

