If a homozygous tall pea plant is crossed with a homozygous short pea plant, explain how the offspring always result in tall pea plants. If two heterozygous tall pea plants are crossed, what percent of the offspring will probably be short?
1 Answer
25% of the heterozygous cross are short, and the offspring of a homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive pea plant will always display the dominant trait (phenotype), because they are heterozygous.
Explanation:
In this explanation, I'm assuming that the allele "T" for tall plants is dominant to the allele "t" for short plants, like in Gregor Mendel's pea plant experiment.
A homozygous tall pea plant will have the genotype "TT" and a homozygous short plant will have the genotype "tt" because homozygous means that both alleles are identical. Since "T" is dominant over "t", any plant with at least one "T" allele will be tall (the dominant trait), regardless of what the other allele is. Let's look at a Punnett square for this cross:
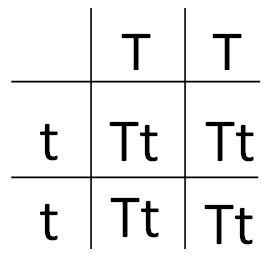
Each of the offspring has one "T" allele, so they are all tall plants. This is because the "T" allele is dominant over the "t" allele, so a plant with one "t" allele and one "T" allele will only display the traits of the "T" allele, which in this case is a tall pea plant.
If we cross the offspring, we get a Punnett square that looks like this:
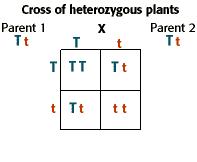
The "TT" and "Tt" crosses both have at least one "T" allele, so they are tall plants. However, the last cross "tt" doesn't have any "T" alleles and is short, because it is homozygous recessive . Since 1 out of 4 pea plants are short, or 1/4, the probability of a short pea plant from a heterozygous cross is 25%.

