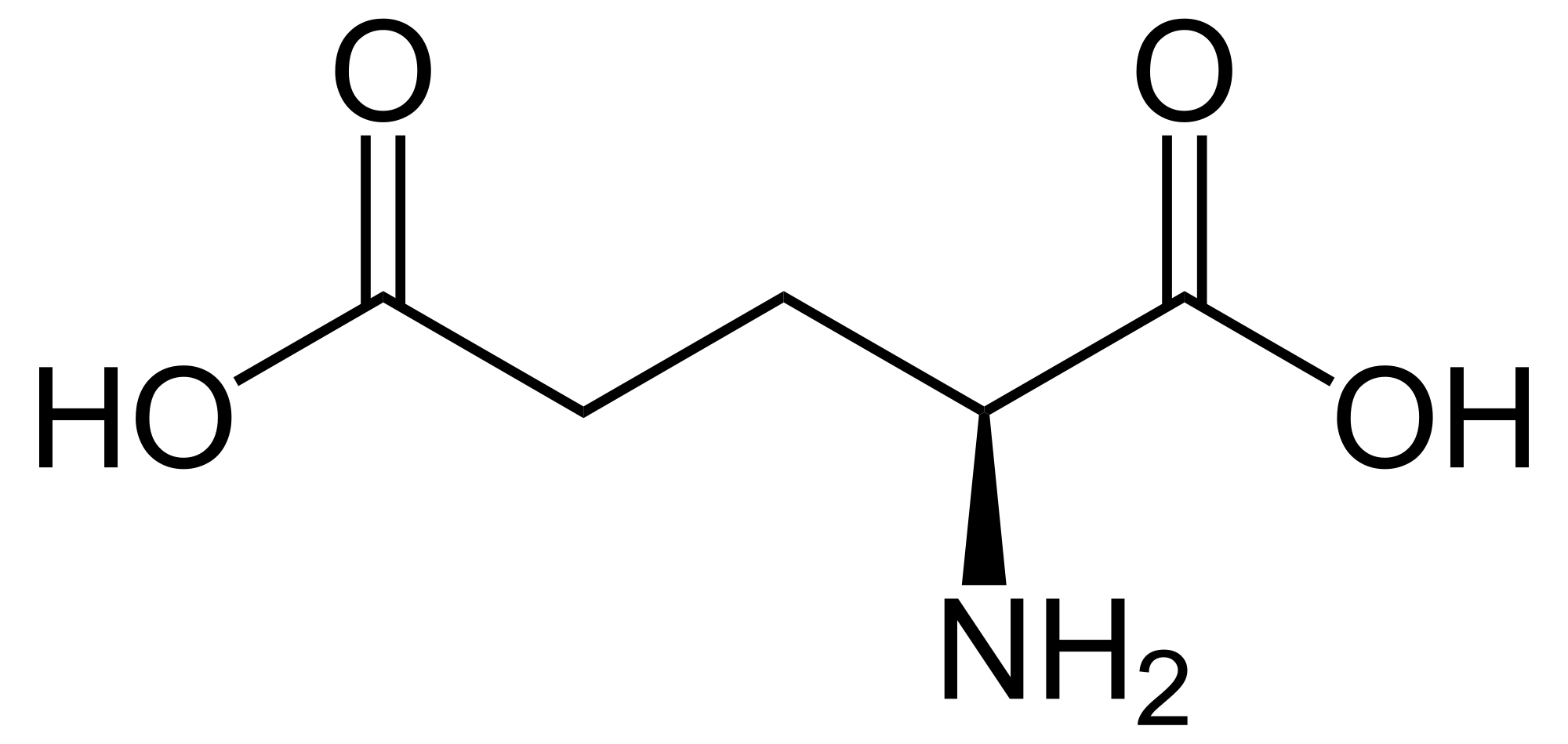
Glumatic acid is an alpha #alpha-# amino acid with the with the formula #color(darkgreen)("C"_5"H"_9"O"_4"N"#.
It is usually abbreviated as #"Glu or E"# in biochemistry. Its molecular structure could be idealized as#" HOOC-CH"_2-"COOH"#, with two carboxyl groups -COOH and one amino group -#"NH"_2#
It contains an #color(red)(alpha - "group"# which is the protonated #color(blue)("NH"_3^+# present when this acid is at its isoelectric point and in acidic medium
It contains an #color(red)(alpha-"carboxylic acid group"# which is the deprotonated #color(purple)("COO"-# present in #"basic and at"" its isoelectric point"#
Before the dissociation takes a reaction within the solution takes place.
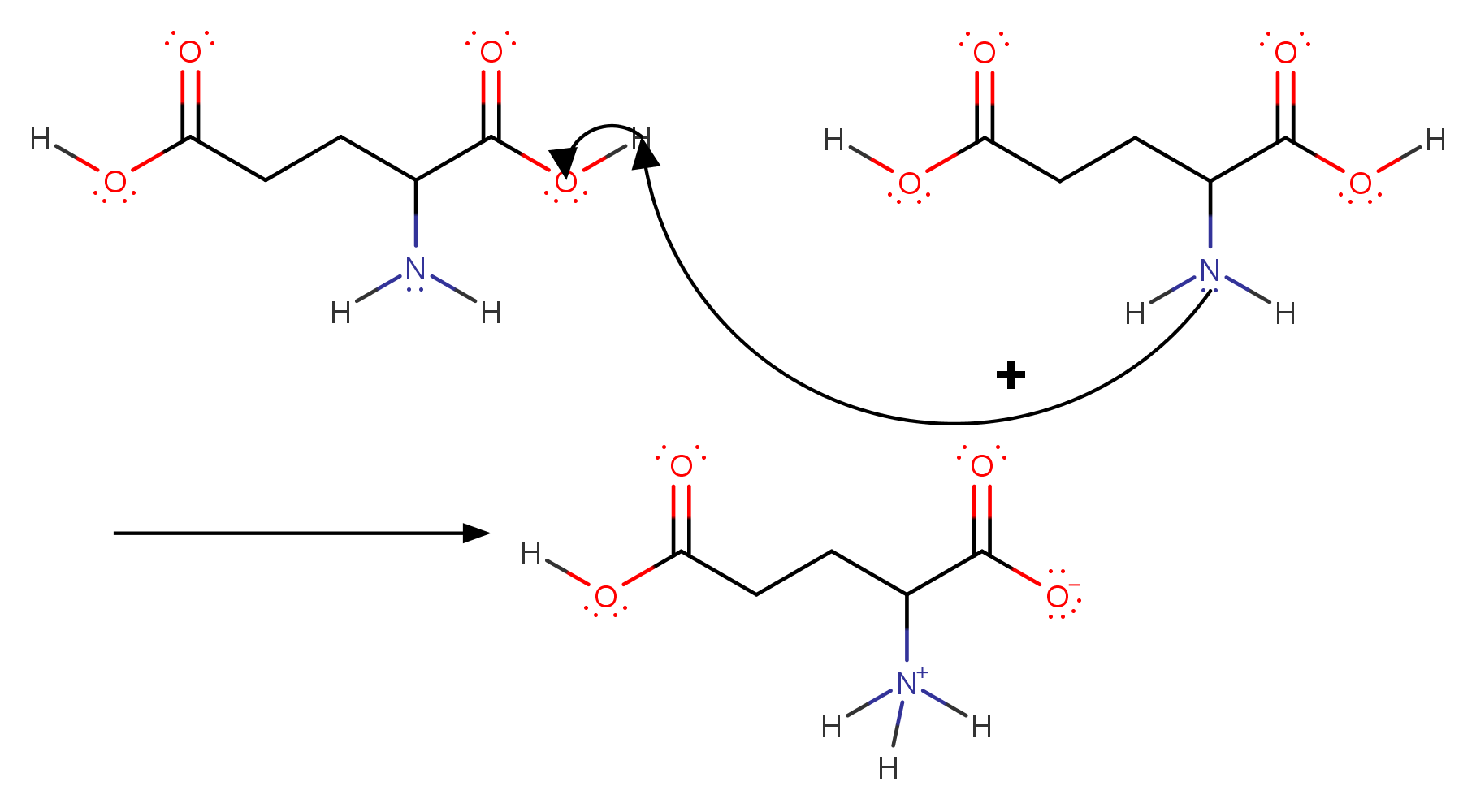
This is the zwitterion of this acid. A zwitterion is a compound with no overall electrical charge, but which contains separate parts which are positively and negatively charged. Protonation of the #color(blue)(alpha - "group"# is followed by deprotonation of #color(red)(alpha-"carboxylic acid group"#
Using the #"pKa's"# to find out the isoelectric point
#("pKa"_1 + "pKa"_2 + "pKR")/3 = (2.19 + 9.67 + 4.25)/3 = 5.37#
This gives us an assumption that at #"pH"=1# the solution will be positive , at #"pH" = 7# it'll be negative and at #"pH" = 13# it will may yield a charge of #-2#
pH = 1
Now that we know the solution will be positive at #"pH"=1#.Let us determine the reaction.
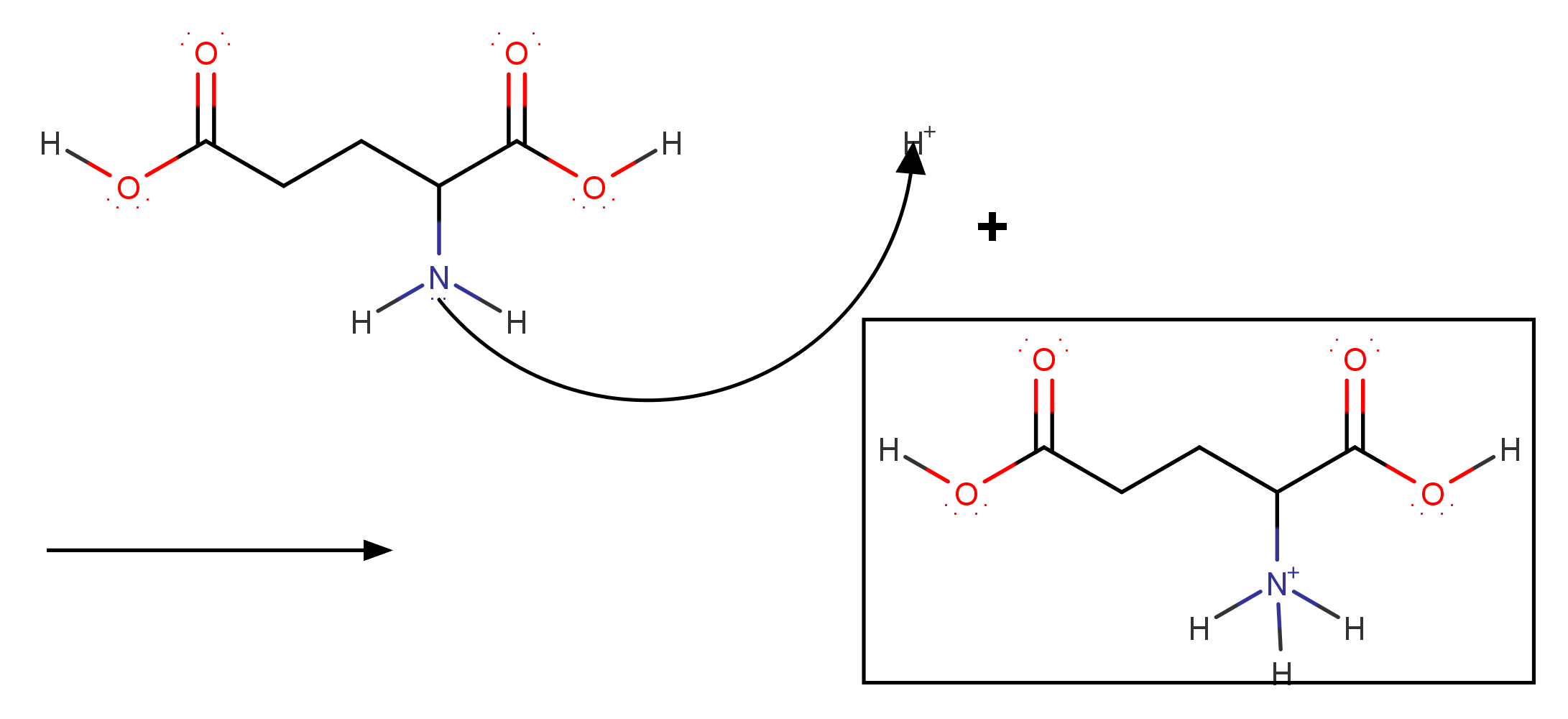
The total charge of #color(maroon)("1,3‐dicarboxypropan‐1‐aminium")# is #+1#
In the second case when #"pH"= 7# the solution is negative but not as negative as #"pH"=13#.
pH = 7
First look at the amino acid carefully.
Did you notice another carboxyl acid which can also be negative due to acid base dissociation? .
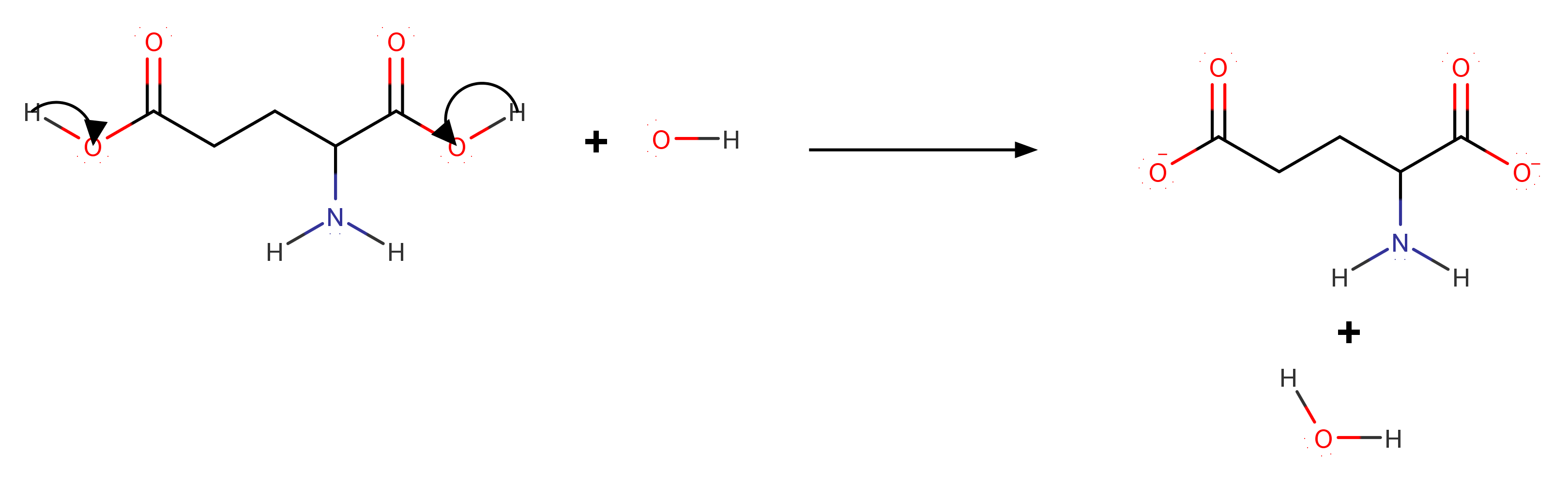
At #"pH"=7 # all the possible acid base dissociation will take place.
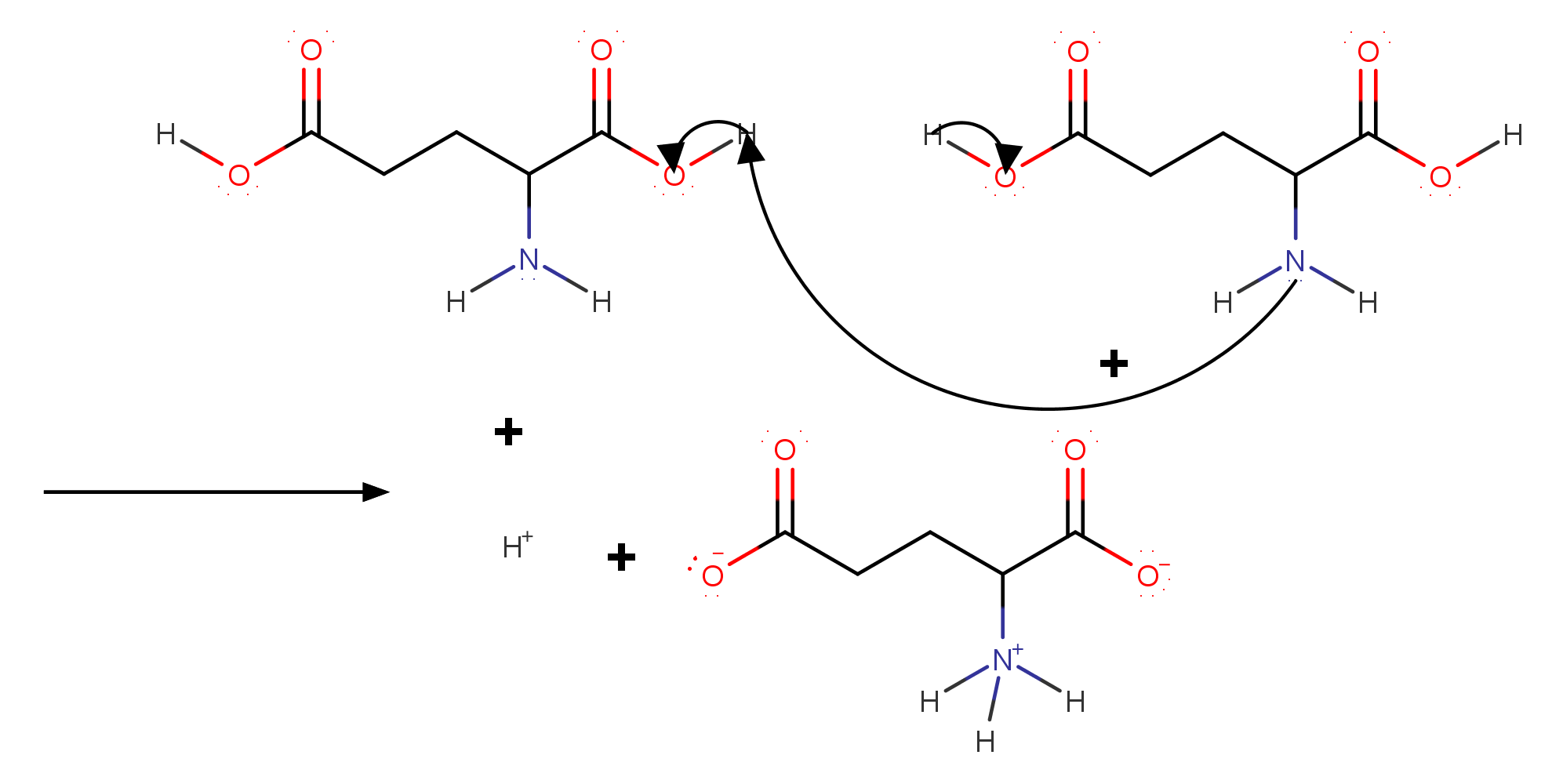
Here also Protonation of the #color(blue)(alpha - "group"# is followed by deprotonation of #color(red)(alpha-"carboxylic acid group"# and in addition to that the additional #"R"-"group"# will also dissociate.
Commonly known as glutamate monoanion it's #"IUPAC"# name is #color(maroon)("2‐azaniumylpentanedioate")#
#"Total charge" = "COOH"^-) + "NH"_3^+ + "COOH"^-#
#= -1 + 1 -1 = -1#
pH = 13
At #"pH" = 13##color(blue)(" NH"_2 color(white)(lll)cancel(rarr)color(white)(lll) "NH"_3^+)#
Because as soon as the #color(purple)("COOH"# dissociates to give #"H"^+# it immediately becomes #"H"_2"O"# because of the increased presence of #"OH"^-# in basic solutions
This is commonly known as glutamate(2‐) or glutamate dianion but the preferred #"IUPAC"# name is #color(maroon)("2‐aminopentanedioate")#
#"Total charge" = color(purple)("COO"^(-) + "COO"^-)#
#-1 -1 = -2#






