Question #4996b
1 Answer
Feb 14, 2018
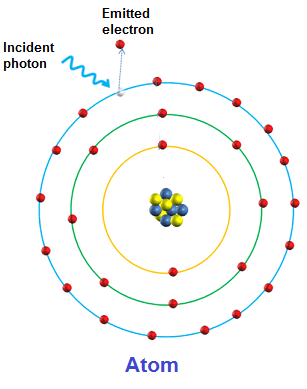
Commonly referred to as the absorption (taken in) of a photon that leads to the emission (given out) of an electron from a material.
Explanation:
Each photon of light contains a specific amount of energy. In a substance, if an electron absorbs the energy of a given photon then the electrons energy state will rise.
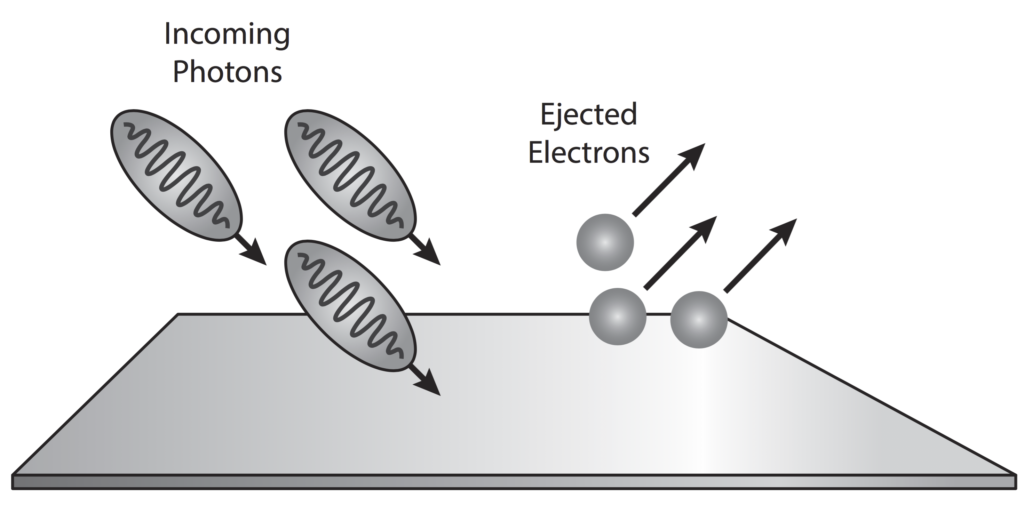
If the electrons energy level rises enough, the electron binding energy (amount of energy 'holding' electrons in place) can be overcome and the electron 'liberated' and thus leaves the substance (emission). In metals, the presence of delocalised electrons as a result of metallic bonding, this process occurs more frequently.