What happens to a cell as it is placed in a hypertonic solution?
2 Answers
A cell loses its *
Explanation:
Hypertonic solution is the one which contain more concentration of solutes as compared to the concentration of solutes in cytoplasm of cell. Which means that a solution contains less water as compared to the water within the cell.
So, When cell is placed in this kind of solution then water
The image below manifests: what happens to red blood cells when it's placed in hypertonic solution?
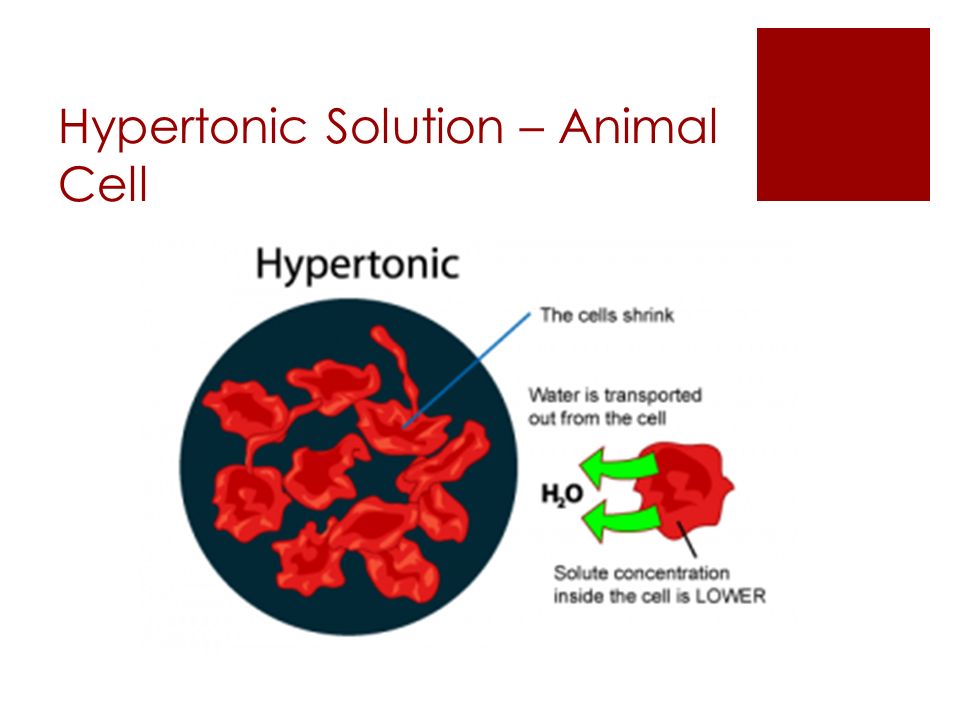
Hope it helps!
Refer to the explanation.
Explanation:
We usually talk about water molecules in cells placed in a hypertonic solution. A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of dissolved solutes, and a lower concentration of water compared to the cell. Since the cell membrane is semi-permeable, not all solutes can cross the cell membrane, but water can always cross the cell membrane.
So, water will move from the cell to the hypertonic solution from where it is in higher concentration (in the cell) to where it is in lower concentration (in the solution). This process is called osmosis.
When an animal cell, such as a red blood cell, loses water to the hypertonic solution, it shrinks, or crenates. If the concentration difference is great enough, the cells can die.
This is why our bodies work to maintain homeostasis, so that the blood and tissue fluid surrounding our cells will be isotonic (equal concentration of dissolved solutes and water) to the cells. This is a very important function of the kidneys.
When plant cells are exposed to a hypertonic solution, their cytoplasm shrinks, which is called plasmolysis, but they don't crenate because of their rigid cell walls.


