What is a gram stain and when is it useful?
1 Answer
Gram stain is an inexpensive and most effective method to differentiate b/w gram positive and gram negative bacteria.
Explanation:
Hans Christain Gram was the first person who used gram staining technique to differentiate b/w gram positive and gram negative bacteria. This method is also known as differential stain.
Following is concept to steps of gram stain procedure:
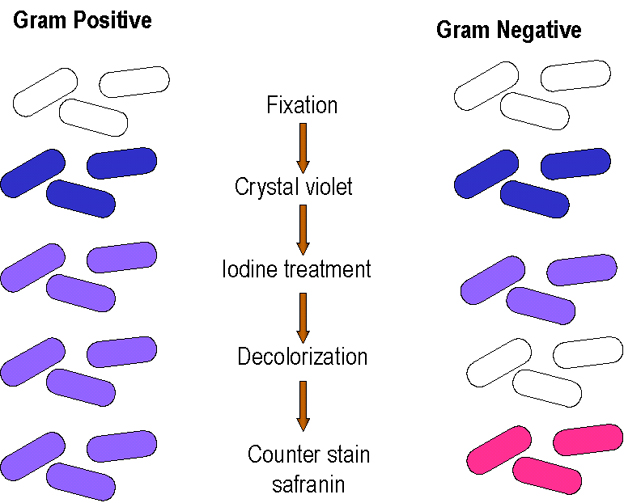
-
Heat Fixation:
In#1^(st)# step, slide with biological sample containing two classes of bacteria(gram -ve & +ve) is passed through a flame. So that bacteria properly stick to the surface of slide. -
Crystal-violet dye(Primary dye):
In#2^(nd)# step, heat fixed sample of bacteria is stained with a crystal-violet#(CV^+)# dye . The crystal violet dye(a purple colour dye) interact with peptidoglycan layer of both gram positive and gram negative bacteria and render them with#color(purple)("purple")# colour. -
Gram's iodine(Mordant):
In#3^(rd)# step, gram's iodine(a solution potassium iodide and Iodine) is added. Iodine is negatively charged i.e#I^-# . Thus, it gets attached to positively charged#CV^+# and form#"CV-I"# complex. Hence, it enhances affinity of bacterial cells for primary dye. In simple words, it help crystal violet dye to link properly with peptidoglycan layer in bacterial cell walls or fixes primary dye. -
Decolorisation solution:
In#4^(th)# step, a decolorizing solution i.e ethyl alcohol or acetone is added to sample. This will wash out the crystal violet dye from gram negative bacteria while gram positive bacteria will retain#color(purple)("primary dye")# . The reason is: gram positive bacteria have#50%# peptidoglycan while cell wall of gram negative bacteria constitutes#10%# peptidoglycan(considering dry weight). This, thinner peptidoglycan layer of gram negative bacteria is easily degraded and bacteria lose the primary dye. -
Safranin(counter stain):
In#5^(th)# #&# final step,#color(hotpink)("safranin")# is added for further distinction b/w two types of bacteria. The gram negative bacteria bearing no colour are stained#color(hotpink)("pink")# after it's addition while gram negative bacteria having their thick peptidoglycan layer retain the purple dye at the end of procedure.
Hope it helps!

