How do you find Polarity?
1 Answer
Uneven dipole moments in an asymmetrical molecule...
Explanation:
Polarity happens when a molecule has a partially positive end and a partially negative end. This happens when the bond between atoms has a big electronegativity difference.
For example, in ammonia
Here is a picture:
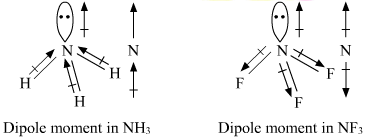
As you can see here, the nitrogen pulls the hydrogens' electrons, which therefore leaves a positive charge on one end of the molecule (the hydrogens), and a negative charge on the other end (the lone electrons of nitrogen).

