What is glycolysis and its importance?
1 Answer
Glycolysis is the sequence of reactions for the breakdown of glucose to two molecules of pyruvic acid under aerobic conditions; or lactate under anaerobic conditions, with the production of energy.
Explanation:
Image source: laboratory info.com(glycolysispng)(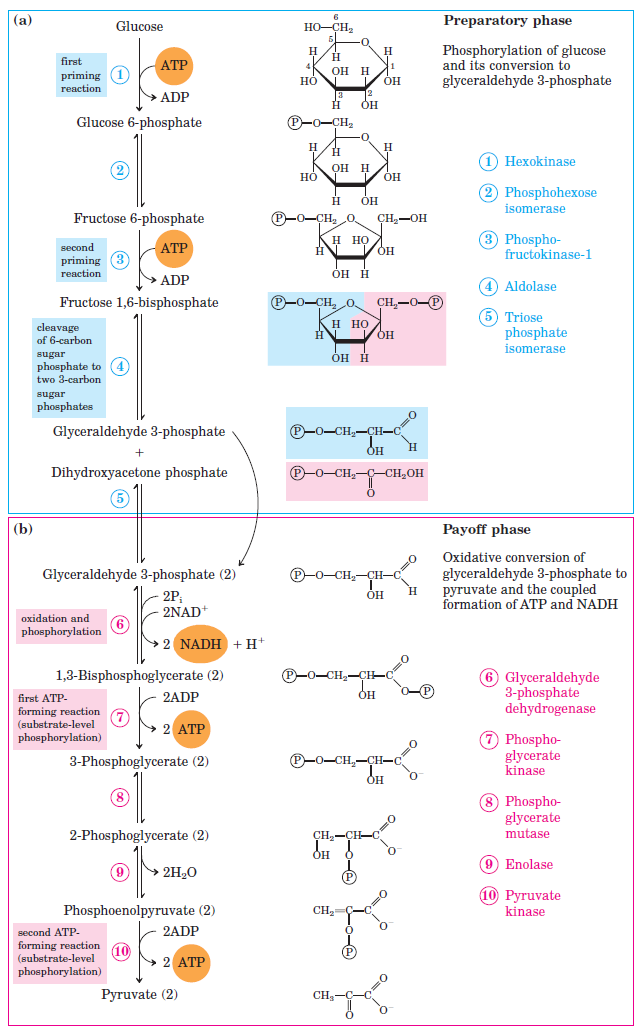 )
)
Glycolysis is an almost universal central pathway of glucose catabolism occurring in the cytoplasm of all the tissues of biological systems, leading to generation of energy in the form of ATP for vital activities. Glycolysis is important in the cell because glucose is the main source of fuel for tissues in the body. Overall glycolysis produces two pyruvate molecules, a net gain of two ATP molecules and two NADH molecules.
Glycolysis is also known as Embden-Meyerhof pathway. Significance of glycolysis is as under:
1) it is the only pathway that is taking place in all the cells of the body
2) it is the only source of energy in erythrocytes as they do not have mitochondria and are not capable of aerobic respiration.
3) during strenuous exercise, when muscle tissues lack enough oxygen, anaerobic glycolysis forms the major source of energy for muscles.
4) this pathway is considered as the preliminary step before complete oxidation
5) it provides carbon skeleton for synthesis of non essential amino acids as well as glycerol part of fat.
6) most of the reactions of the glycolytic pathway are reversible, which are also used for gluconeogenesis.

