How is protein synthesis different from DNA replication?
2 Answers
Well, the name itself...
Explanation:
Protein synthesis is the process of the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and ribosomes working together to make proteins. It requires energy and
Protein synthesis makes proteins, while
To read more, visit:
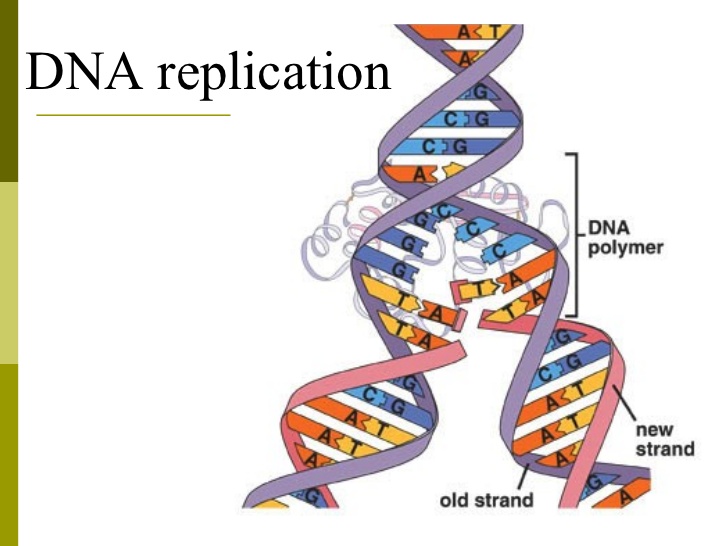
DNA replication occurs in the nucleus and produces two identical sets of DNA.
Protein syntheses produces mRNA, which is then translated by tRNA molecules carrying amino acids to produce a polypeptide or protein.
Explanation:
DNA replication is the process in which the DNA is copied before mitosis or meiosis. The results of DNA replication are two identical copies.
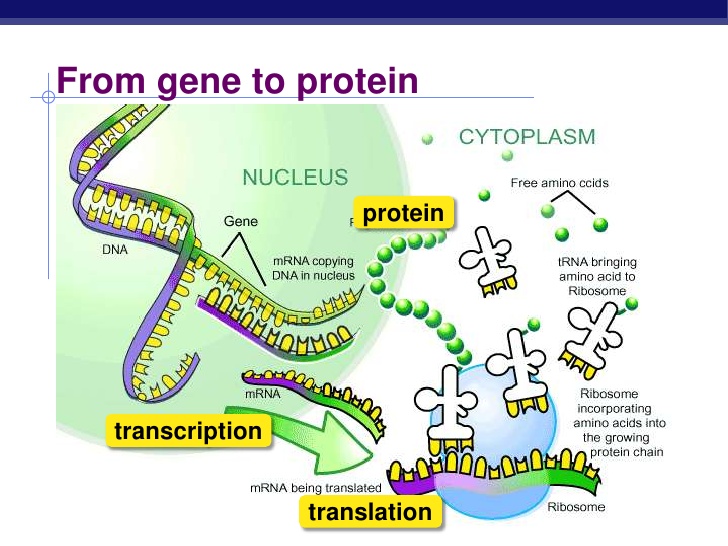
Protein synthesis occurs in two steps, transcription and translation. Transcription is the process in which segments of DNA (genes) are transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the cell nucleus.
The mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to ribosomes in the cytoplasm or rough endoplasmic reticulum, where it will be translated into a chain of amino acids making a polypeptide or protein. This occurs when transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules carrying amino acids bring amino acids to the ribosome according to the codons on the mRNA. The tRNA molecules have anticodons which correspond to the mRNA codons, which ensures that the amino acids are arranged in the correct sequence.