How do you test for water?
3 Answers
Using pH meter, dissolved oxygen meter, electrical conductivity meter, ICP-MS, TXRF, etc.
Explanation:
There are different water quality parameters.
pH shows acidity or alkalinity of water. A pH meter shows hydrogen ion concentrations of water
Most drinking water standards state that pH should be between 6.5 and 9.5 (7 is neutral). In some countries that can be different.
Dissolved oxygen can be measured dissolved oxygen meters. Although air contains approximately 21% oxygen gas, water contains very limited amount of oxygen gas due to oxygen consuming contaminants, high temperature and low pressure. Oxygen is measured by haldheld dissolved oxygen meters. If your dissolved oxygen is around 10 mg per Liter (it is good) in water and ecosystem balance.
There are other parameters to provide facts about water quality such as dissolved solids, suspended solids, turbidity, etc.
If you wonder elemental composition of water, ICP (Intercoupled plasma) or TXRF (total X-ray fluorometric spectroscopy) or other scientific equipment can be employed.
For synthetic (or human made) chemicals (chlorinated hydrocarbons for example) GC (gas chromatography) is one of the most commonly used equipments.
Testing water existence
Explanation:
Some plants (i.e. reeds) live in suitable environments in terms of water. By visual observation, one can tell whether water is available or not.
However, for groundwater sources, there are some water detection methods. One of these methods is resistivity.
Resistivity is defined as the resistance to current flow as a result of an applied electric potential. Resistance is measured in ohms. Resistivity is resistence times legnth (such as
In geophysical surveys resistivity is determined as the electrical resistance per length of a unit cross section area (
Resistivity below ground zero is a function of material type, porosity (space between soil particles), water content (within spaces between soil particles) and concentration of dissolved (such as TDS or salts) contaminants in the pore water. Generally, dry soils and rock have very high resistance to electrical flow whereas inorganically contaminated saturated soils have a relatively low resistance.
Other methods are seismic methods, electromagnetic conductance method, ground penetrating radar, and satellite methods, etc.
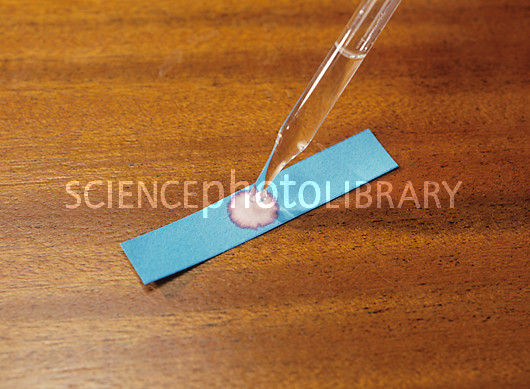
Use anhydrous copper sulfate or anhydrous cobalt chloride paper
Explanation:
Well, the other methods mentions are very good, however I'd like to add some common laboratory methods here as well.
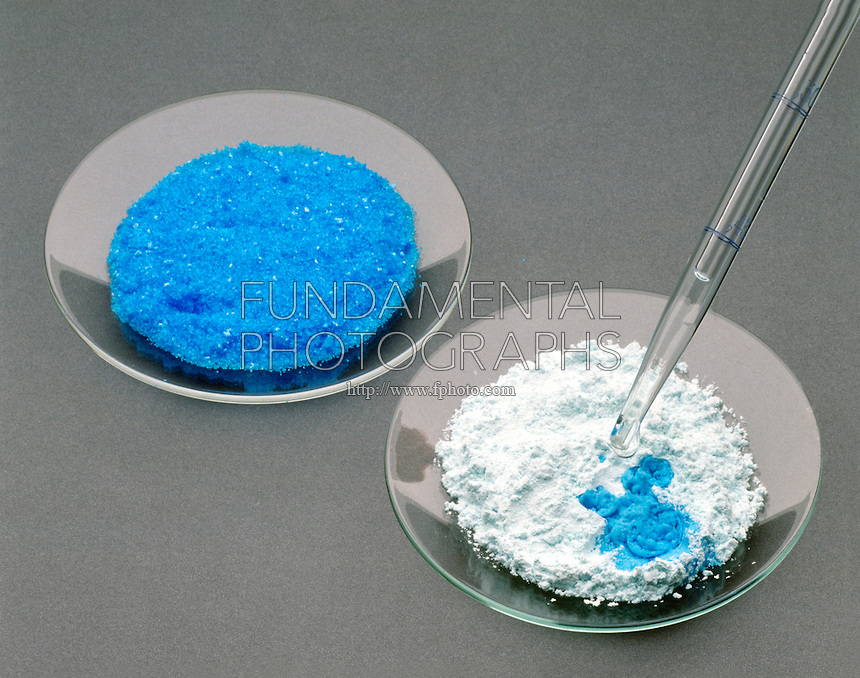
If your lab has copper sulfate crystals
Anhydrous copper sulfate crystals are white in colour, but when they come in the presence of water, they'll turn blue. Have a look here:

Cobalt chloride can also do this, but it'll change from blue (anhydrous) to pink (hydrated). Note that cobalt chloride is more commonly used in the form of paper strips.