What if protein++ comes in urine? Are there any chances of future serious damage? Why does this occur?
1 Answer
Heavy proteinuria usually indicates glomerular disease.
Explanation:
The glomerulus is the proximal part of the nephron and is the main filtration unit in the kidney. It is made up of three principle layers listed in order of proximity to blood:
- Fenestrated endothelium
- Basement membrane
- Podocytes (contain foot processes)
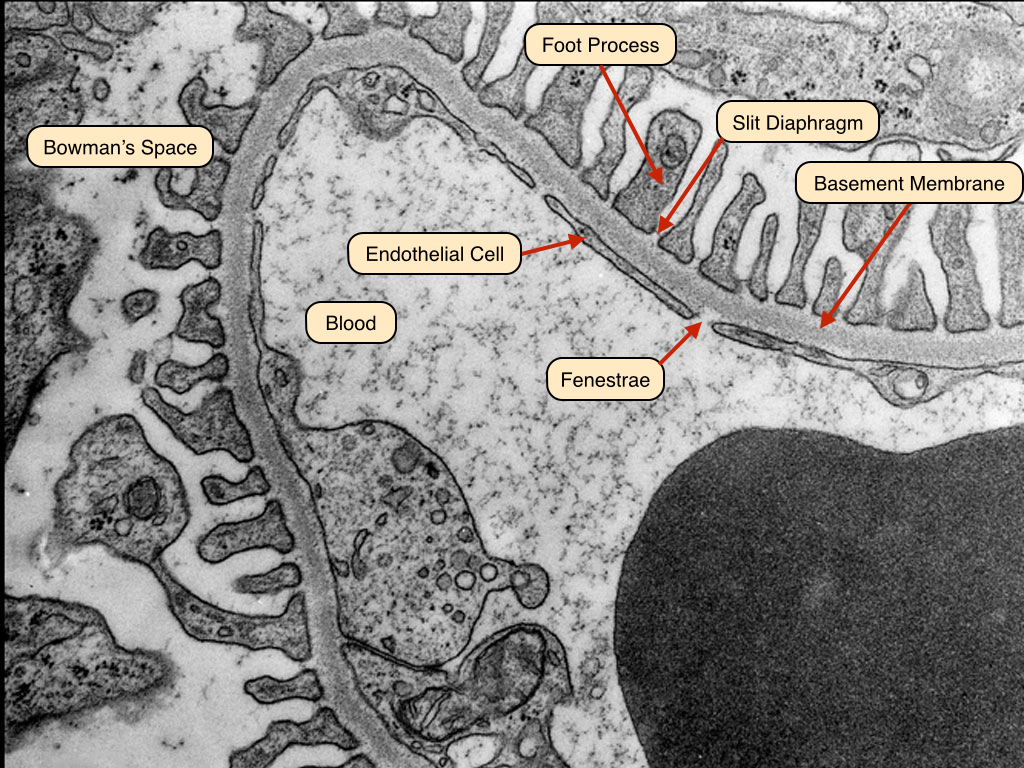
The glomerular basement membrane is negatively charged and repels most negatively charged plasma proteins - preventing them from being filtered into Bowman's space.
Hence, if the GBM is damaged, proteins will be found in the urine.
Nephrotic syndromes are associated with:
- Heavy proteinuria (>3.5 g/day)
- Hypoalbuminemia (< 3 g/dL)
- Generalized edema
- Hyperlipidemia
- Lipiduira
and are caused by damage to the GBM through a variety of mechanisms.
Some diseases which lead to a nephrotic syndrome include:
- Minimal change disease
- Focal segmental glomerular sclerosis
- Membranous glomerulonephritis
- Diabetic nephropathy
- Amyloidosis
Each of these diseases has its own pathophysiology and prognosis. For example, MCD is usually a childhood condition and is often benign, however, diabetic nephropathy can lead to a continuous decline in glomerular filtration and associated hypertension.

