What are the factors that make amphoteric oxides able to react with both acids and alkalis?
1 Answer
Warning! Long Answer. Here's what I find.
Explanation:
Basic oxides
Metallic character increases from right to left and from top to bottom in the Periodic Table.
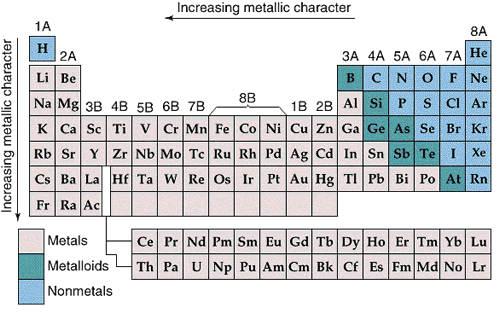
The most metallic elements form the most basic oxides.
Even if the oxides are insoluble in water, we still call them basic oxides because they react with acids.
Acidic oxides
Nonmetallic character increases from left to right and from bottom to top in the Periodic Table.
The most nonmetallic elements form the most acidic oxides.
They react with water to form oxoacids. For example,
Even if an oxide is insoluble on water, we still class it as acidic if it reacts with bases to form salts. For example,
Amphoteric Oxides
Some oxides react with both acids and bases, that is, they are amphoteric.
For example,
The lighter elements of Groups 2 and 13, some of the
The most basic oxides are at the lower left of the Periodic Table, and the most acidic oxides are at the upper right, so it is not surprising that the borderline between acidic and basic oxides occurs along a diagonal.
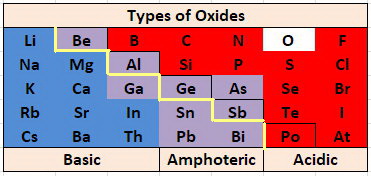
Amphoterism and oxidation states
Amphoterism depends on the oxidation state of the oxide.
There is no simple way to predict which elements will be amphoteric.
The amphoteric character of an oxide probably reflects the ability of the metal to polarize the surrounding oxide ions, that is, to introduce a significant covalent character into the
This ability increases with oxidation state as the positive character of the central atom increases.
However, in Group 15, only the oxides with lower oxidation states are amphoteric.
The oxides with higher oxidation states are too acidic to be amphoteric.
Many transition metals form amphoteric oxides, but it is difficult to predict which of their oxides will be amphoteric.
One thing we can say is that the amphoteric nature of an oxide depends strongly on the oxidation number of the metal.
The acidity of a cation rises rapidly with charge, so transition metals with a variety of oxidation numbers may have oxides that are acidic, basic, or amphoteric.
The higher the oxidation number, the more acidic the corresponding oxide.
For example, chromium forms three oxides.
It dissolves in acid to produce hydrated chromium(III) ions,
It dissolves in a concentrated base to form hydrated tetrahydroxochromate(III) ions.

