Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
Key Questions
-
Answer:
The central dogma describes how a gene is ultimately expressed.
Explanation:
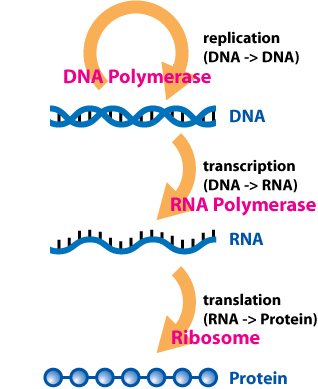
The central dogma shows how information is transferred from DNA to RNA to protein; when the cell receives a signal that a gene must be expressed, RNA Polymerase is recruited to the region of DNA where that gene is located. It makes an RNA copy of that region of DNA, in a process called transcription.
This RNA is then transported out of the nucleus of the cell, and is "translated" into a protein by molecular machines called ribosomes. The process of going from DNA (gene) to RNA to protein is basically gene expression.
-
DNA -> DNA -> RNA -> protein
DNA -> DNA
(the process of DNA copying itself is called replication)DNA -> RNA
(the process of DNA being used to create RNA is called transcription)RNA -> protein
(the process of ribosomes using RNA molecule to make proteins is called translation)Here is a video which summarizes the central dogma of molecular biology using DNA Workshop from PBS.
video from: Noel Pauller