2.5x10-3 moles of solid Mg(OH)2 is added to a 100.0 mL sample of 0.250 M aqueous chlorous acid solution. Ignore the volume change associated with the added solid. Find the pH of the solution?
Use the information below to answer the following question:
2.5x10-3 moles of solid Mg(OH)2 is added to a 100.0 mL sample of 0.250 M
aqueous chlorous acid solution. Ignore the volume change associated with the
added solid. Find the pH of the solution.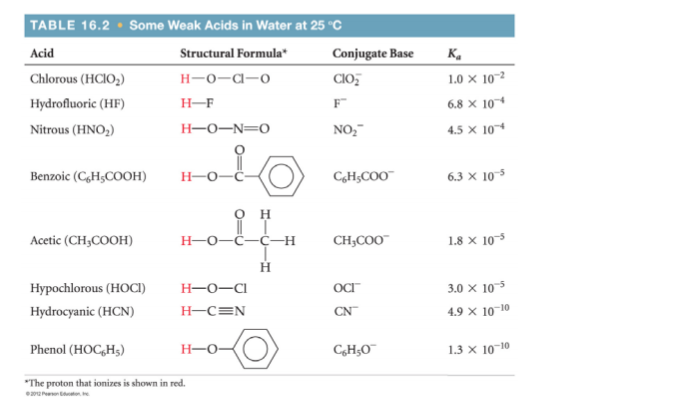
Use the information below to answer the following question:
2.5x10-3 moles of solid Mg(OH)2 is added to a 100.0 mL sample of 0.250 M
aqueous chlorous acid solution. Ignore the volume change associated with the
added solid. Find the pH of the solution.
1 Answer
Explanation:
The base is neutralised by the acid:
The number of moles of chlorous acid is given by:
We are told that:
From the stoichiometry of the reaction we can see that the number of moles of
So the number remaining is given by:
We can also say that the number of moles of
We have now created an acid buffer since we have a weak acid in combination with its co - base.
Chlorous acid dissociates:
For which:
The concentrations are those at equilibrium.
To find
Since we are told the volume is 100 ml = 0.1 L then the initial concentrations become:
At this point it is common to assume that, because the dissociation is so small then
However, we can't do this in this case as the size of
If we multiply out the expression we get:
This is a quadratic equation which can be solved for
If we make the assumption that

