What is a double replacement reaction? How do you write the molecular and net ionic equations?
1 Answer
Refer to the explanation.
Explanation:
Double replacement reactions, also called double displacement and metathesis reactions involve aqueous ionic reactants, which react to produce an insoluble product (precipitate), an insoluble gas, or water.
The molecular equation shows all of the reactants and products, while the net ionic equation shows only those ions that reacted.
In a double replacement reaction, the positive and negative ions in the reactants switch partners to form the products. The generalized equation is
Practice Problem 1.
Write the molecular equation and net ionic equation for the reaction between silver nitrate,
Solution:
1. Molecular Equation
Neither of the products is water or a gas, so, if the reaction actually occurs, we need to find out if one of the two products is insoluble, or solid, in water. We do this by consulting a solubility table like the following:
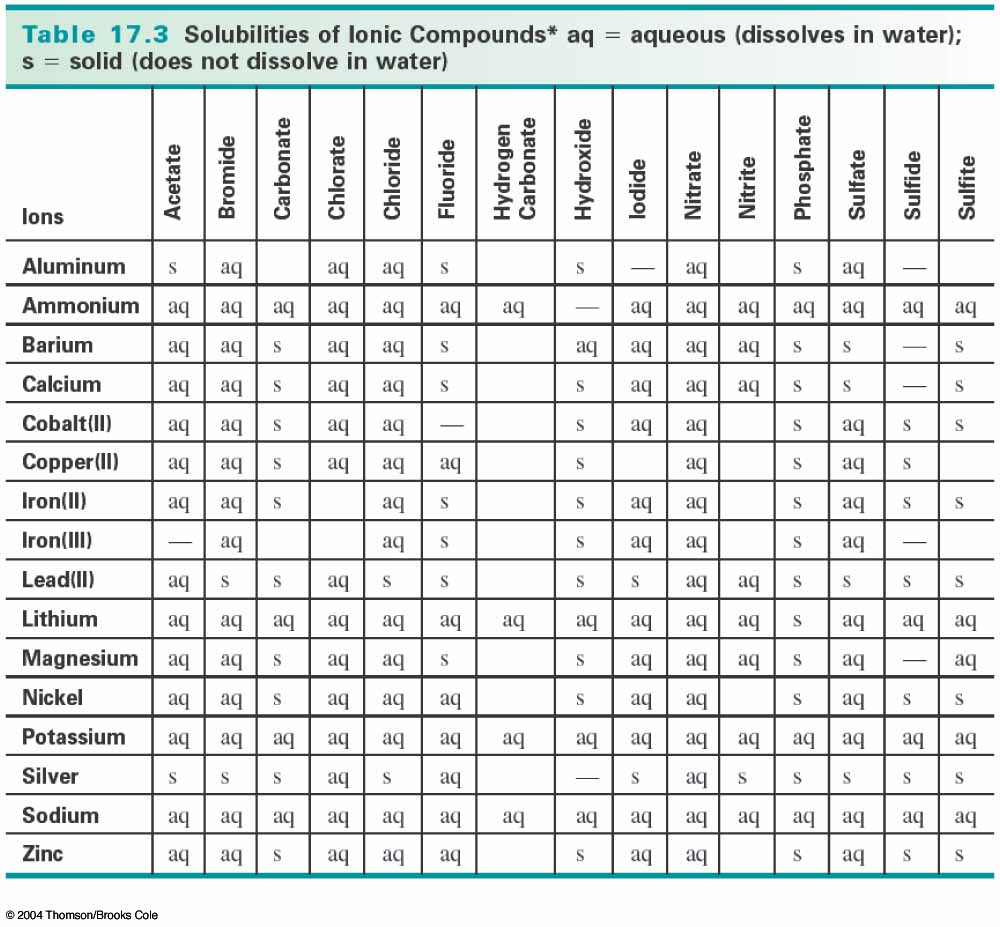
If you look at the chart, find where silver and sulfate intersect, and you will see an "s". This means that silver sulfate does not dissolve in water, so it is a solid. Next find where copper(II) and nitrate intersect, and you will see "aq". This means that copper(II) nitrate does dissolve in water. So now we know that a double replacement did take place, with the insoluble product, silver sulfate (
Now we can complete the molecular equation as:
The down arrow indicates that the solid is a precipitate.
2. Net Ionic Equation.
The net ionic equation involves only those ions that were involved in the formation of the precipitate (solid).

