Question #57594
1 Answer
First you must draw the Lewis structures of these compounds.
Explanation:
Then you use VSEPR theory to predict their shapes.
The number of lone pairs and bond pairs comes automatically from this procedure.
1.
2. Your skeleton structure will have an
3. In your trial structure where every atom has an octet, there will be 26 valence electrons.
4.
5. Insert these electrons as a lone pair on the

Now we use VSEPR Theory.
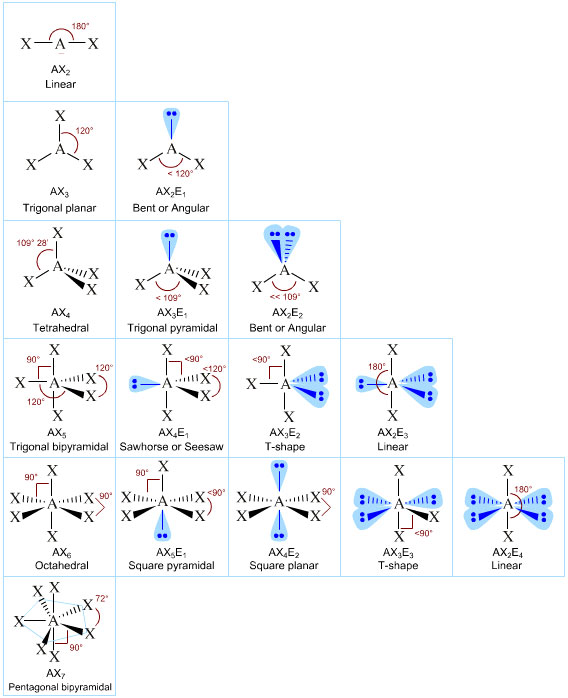
6. This is an
Using the above procedure, you find that your trial structure has 40 valence electrons, but you actually have 42 electrons available.
Your Lewis structure will have 5
This is an

The molecular geometry is square pyramidal.
Now, can you do the rest? If you have difficulties, just post another question.

