Silver nitrate and sodium chloride are both soluble ionic compounds, which means that they actually exist as ions in aqueous solution.
#AgNO_(3(aq)) -> Ag_((aq))^(+) + NO_(3(aq))^(-)#
and
#NaCl_((aq)) -> Na_((aq))^(+) + Cl_((aq))^(-)#
When these two substances are mixed, the silver cations, #Ag^(+)#, and the chloride anions, #Cl^(-)#, will bond together to form silver chloride, #AgCl#, an insoluble solid, which precipitates out of solution.
The other two ions, #Na^(+)# and #NO_3^(-)#, will continue to exist as such in solution, since the potential compound sodium nitrate, #NaNO_3#, is soluble in aqueous solution.
So, the complete ionic equation looks like this
#Ag_((aq))^(+) + NO_(3(aq))^(-) + Na_((aq))^(+) + Cl_((aq))^(-) -> AgCl_((s)) darr + Na_((aq))^(+) + NO_(3(aq))^(-)#
The net ionic equation, which you get by eliminating spectator ions, i.e. the ions that are present on both sides of the eqaution, will be
#Ag_((aq))^(+) + cancel(NO_(3(aq))^(-)) + cancel(Na_((aq))^(+)) + Cl_((aq))^(-) -> AgCl_((s)) darr + cancel(Na_((aq))^(+)) + cancel(NO_(3(aq))^(-))#
or
#Ag_((aq))^(+) + Cl_((aq))^(-) -> AgCl_((s)) darr#
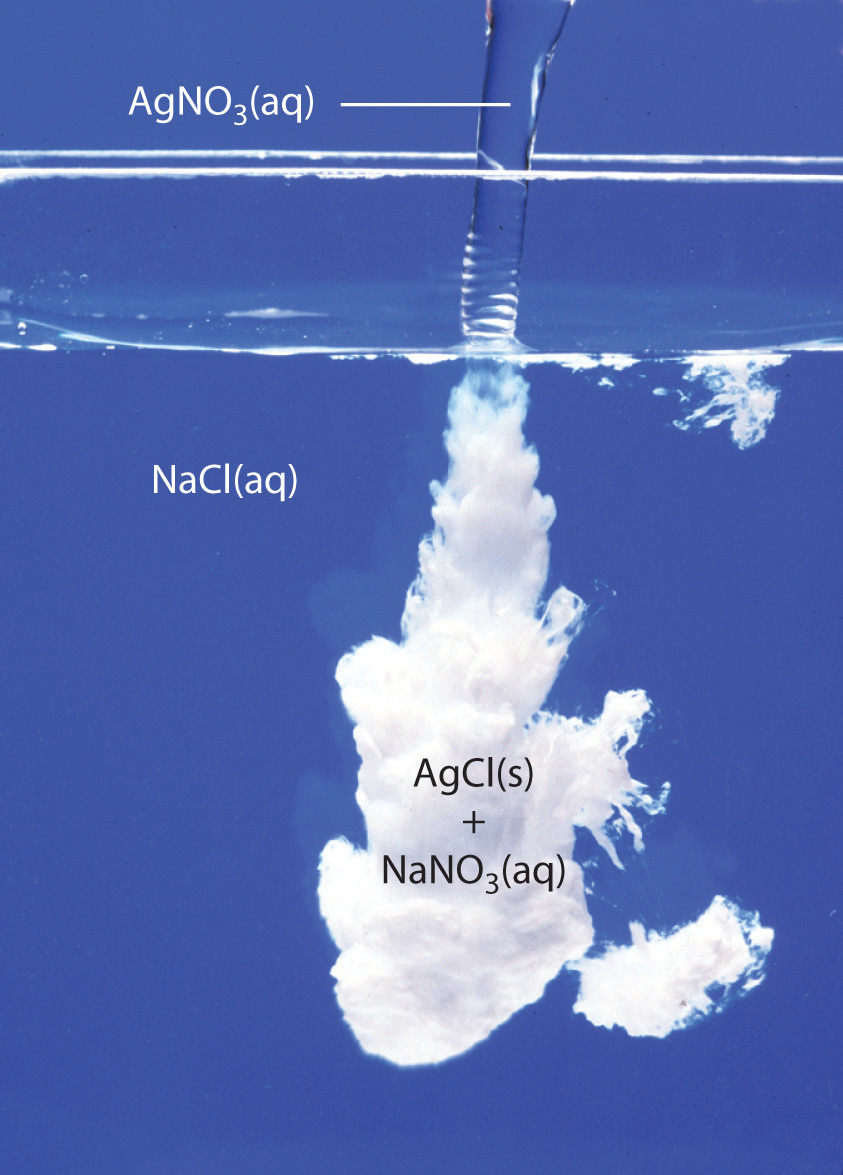
So, as a conclusion, a double replacement reaction takes place in which the silver cations and chloride anions form an insoluble white solid called silver hcloride, #AgCl#.


