Question #13933
1 Answer
Explanation:
Extracellular fluid, or ECF, is being kept at a pH of approximately
["H"^(+)] = 10^(-"pH")[H+]=10−pH
["H"^(+)] = 10^(-7.4) = color(green)(4.0 * 10^(-8)"M")[H+]=10−7.4=4.0⋅10−8M
In the context of extracellular liquid, it's useful to express this value in milimoles per liter, or milimolar
4.0 * 10^(-8)color(red)(cancel(color(black)("moles")))/"L" * (10^3"mmoles")/(1color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mole")))) = 4.0 * 10^(-5)"mM"
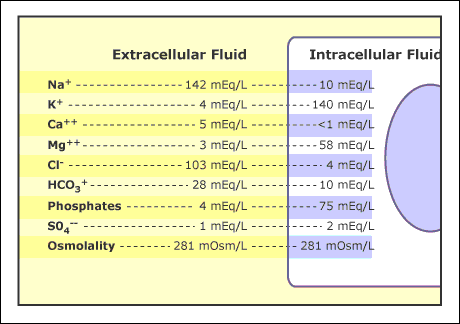
By comparison, the concentration of sodium cations,
["Na"^(+)] = "136-145 mEq/L"
and the concentration of bicarbonate anions,
["HCO"_3^(-)] = "22-28 mM"
 http://anaphyteachushowtoblog.blogspot.ro/2012/01/chapter-23-urinary-system-and-body.html
http://anaphyteachushowtoblog.blogspot.ro/2012/01/chapter-23-urinary-system-and-body.html
For example, the concentration of the bicarbonate anions is
(28color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mM"))))/(4.0 * 10^(-5)color(red)(cancel(color(black)("mM")))) = 7 * 10^5
higher than the concentration of hydrogen ions.
As a cool fact, concentrations of hydrogen ions that either exceed

