Question #a46f8
1 Answer
For part (a)
Explanation:
I'll show you how to solve part (a), and leave part (b) to you as practice.
You're dealing with two neutralization reactions, that take place between a strong acid and a strong base.
In both cases, a complete neutralization requires the consumption of both reactants. However, the products of the reaction will differ.
When a strong base and a strong acid undergo complete neutralization, the resulting solution will contain water,
As you know, strong acids and bases dissociate completely in aqueous solution to form ions
#"HCl"_text((aq]) + "H"_2"O"_text((l]) -> "H"_3"O"_text((aq])^(+) + "Cl"_text((aq])^(-)#
#"NaOH"_text((aq]) -> "Na"_text((aq])^(+) + "OH"_text((aq])^(-)#
When these two solutions are mixed, the reaction vessel will contain - hydronium cations,
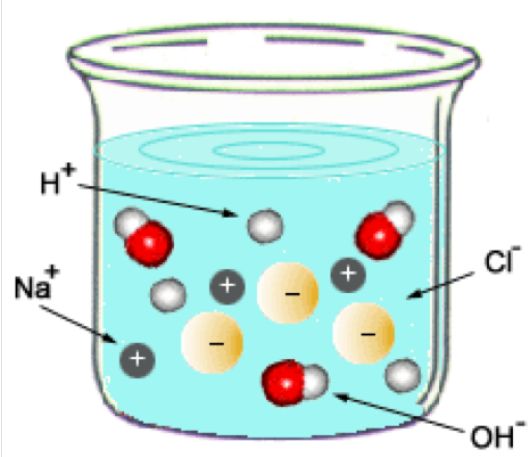
At this point, the hydronium cations and the hydroxide anions will neutralize each other and form water
#"H"_3"O"_text((aq])^(+) + "OH"_text((aq])^(-) -> 2"H"_2"O"_text((l])#
After the reaction is complete, your reaction vessel will contain
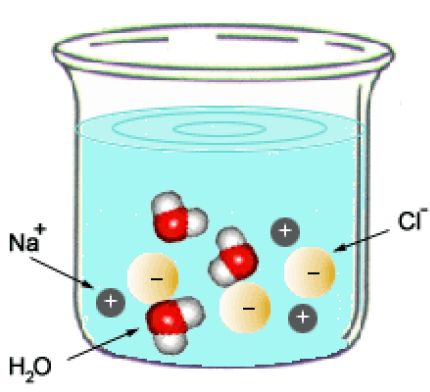
Notice that the two reactants react in a
Use the molarity and volume of the sodium hydroxide solution to determine how many moles it contains
#color(blue)(c = n/V implies n = c * V)#
#n_(NaOH) = "0.250 M" * 20.0 * 10^(-3)"L" = "0.00500 moles NaOH"#
Since both the strong acid and the strong base dissociate in a
This means that you will need a volume of
#color(blue)(c = n/V implies V = n/c)#
#V_(HCl) = (0.00500 color(red)(cancel(color(black)("moles"))))/(0.100color(red)(cancel(color(black)("moles")))/"L") = "0.0500 L"#
Expressed in milliliters, the answer will be
#V_(HCl) = color(green)("50.0 mL")#
You can take the exact same approach for part (b). Start with the balanced chemical equation
#"HClO"_text(4(aq]) + "KOH"_text((aq]) -> "H"_2"O"_text((l]) + "KClO"_text(4(aq])#
Once again, use the

