Question #2b520
1 Answer
The coordination number of an atom in a crystal is the number of its "nearest neighbours".
Explanation:
The atoms in crystals are arranged in various repeating three-dimensional arrays.

The atoms have different numbers of nearest neighbours, depending on how they are packed in the crystal.
The coordination number (CN) is a measure of how tightly the atoms are packed together.
Here are some examples.
The atoms in polonium (
(from 2012books.lardbucket.org)
An atom in a polonium crystal has CN = 6.
You can see its six nearest neighbours in the diagram above.
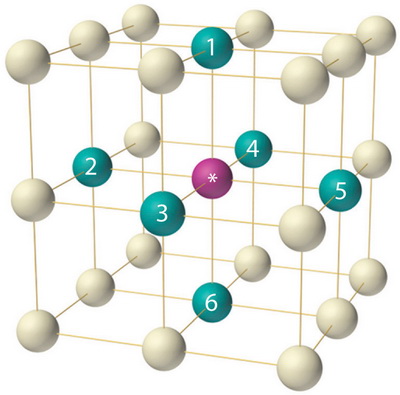
The crystal structure of sodium (

An atom of
Its nearest neighbours are the 8 atoms at the corners of the cube.
The atoms in magnesium (
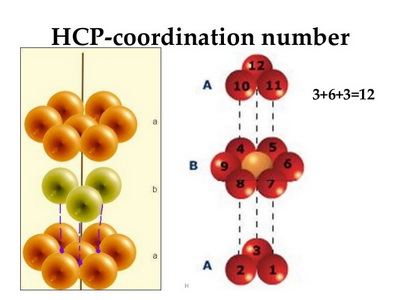
(from www.slideshare.net)
Each atom of magnesium has 12 nearest neighbours, so CN = 12.
The University of Sydney has some great animations that might help you visualise some crystal structures and their coordination numbers.
The video below shows how to find coordination numbers.

