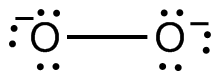Question #9f76a
1 Answer
The peroxide anion.
Explanation:
The idea here is that transition metals can obtain a stable noble gas configuration by forming coordination complexes.
For a given transition metal, its stable noble gas configuration will correspond to the electron configuration of the noble gas with which it shares the period in the periodic table.
Cobalt is located in period 4, so its noble gas electron configuration will match that of krypton,
So, the effective atomic number for a transition metal in a coordination complex is calculated like this
#color(blue)("EAN" = Z - "O.N." + n xx 2)" "# , where
Now, your goal here is to use this equation to find the oxidation state of the transition metal. This will then allow you to find the charge,
Your transition metal cation will be surrounded by
- two ammonia molecules,
#"NH"_3# - one ethylenediamine molecule,
#"en"# - one unknown ligand labeled
#"O"_2^(x)#
Now, it is important to realize that ethylenediamine and the
This means that the coordination number of the metal cation, which essentially tells you how many atoms are donating electrons to the metal cation, will be equal to
#2 xx "NH"_3# #2 xx "en"# #2 xx "O"_2^(x)#
So, plug this into the equation for EAN and find the oxidation state of the metal
#"EAN" = 27 - "O.N." + 6 xx 2#
#"O.N." = 27 + 12 - 36 = +3#
Now, notice that you're dealing with a neutral coordination compound made up of
#["Co"("NH"_3)_2"O"_2^(x)("en")]^(y+)" "# and#" ""Cl"^(-)#
This tells you that the overall charge of the complex ion,
#(y+) + (1-) = 0 implies y = 1+#
Now, ammonia and ethylenediamine are neutral molecules, which means that the overall charge on the
#"O.N." + overbrace((1 xx x))^(color(purple)("one O"_2color(white)(a)"ligand")) + overbrace(1 xx (1-))^(color(blue)("one Cl"^(-)"anion")) = 0#
This is equivalent to
#x = 1 - (+3) = -2#
Therefore, you're dealing with the