Question #61660
5 Answers
Here is the answer to #3. (I can't really make out the other questions!)
Explanation:
These two exceptions to the usual observation that ionization energy increases across a row of the periodic table occur for two different reasons.
Remember that ionization energy (IE) is the energy required to remove the highest-energy electron from the atom (the one in the orbital of highest energy).
In Mg, this is a
For sulfur, the reason is evidence of Hund's rule, which states that when electrons populate the identical energies of the
With sulfur, we have the first instance of an electron pair being created in the
Here's my answer to Question 1.
Explanation:

I would expect the energy level diagram to look like the one below.
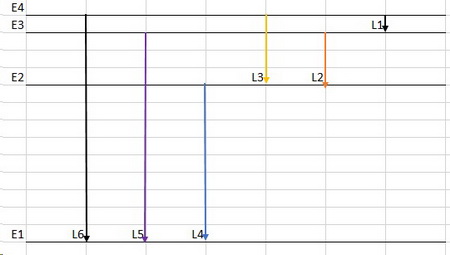
There are only six allowed transitions.
The shortest line (L1) corresponds to the infrared, and the longest line (L6) corresponds to the ultraviolet.
Lines L2 to L4 correspond to increasingly shorter wavelengths in the visible spectrum in the order
Here's my answer to Question 2.
Explanation:
We need to refer to a Periodic Table for this question.
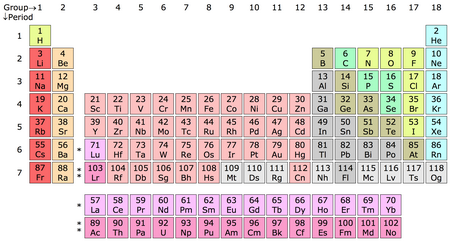
(From Wikipedia)
a.
We would predict its electron configuration to be
However, because of the stability of half-filled subshells, an electron is "promoted" to the
The actual electron configuration is
b.
Its electron configuration is
c.
We would predict its electron configuration to be
However, because of the extra stability of a filled shell, an electron is "promoted to the
The actual electron configuration is
d.
When removing electrons to form ions, we remove the
The electron configuration of
e.
The electron configuration of
f.
Its electron configuration is
When forming the cation, we remove the
The electron configuration of
Here's my answer to Question 3.
Explanation:
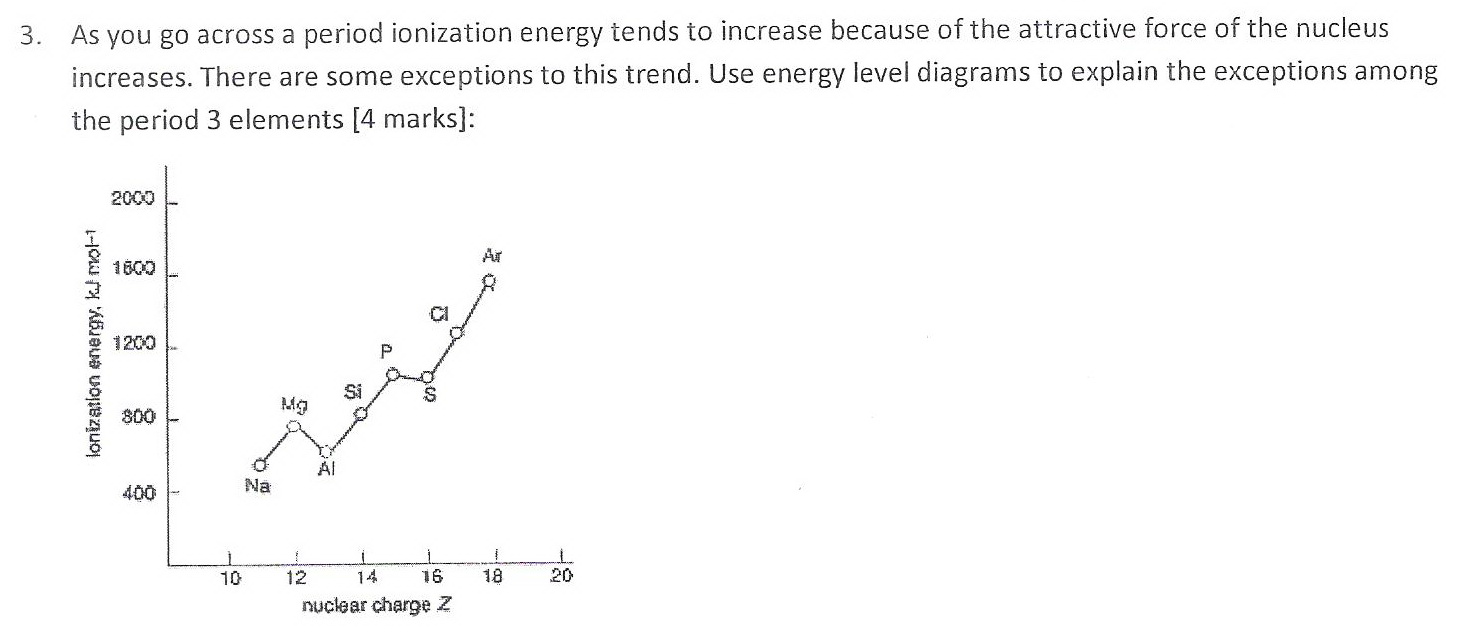
The "dips" in the curve are not because the ionization energies of
The energy level diagram for

The
Hence, more energy is required to remove an electron from this level, and the ionization energy is higher.
The energy level diagram for
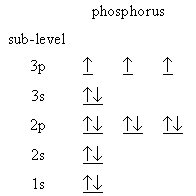
(Adapted from Creative Chemistry)
Here, the
Hence, more energy is required to remove an electron, and the ionization energy is higher than expected.
Here's my answer to Question 4.
Explanation:

a. Energy level diagrams
The electron configuration of
In the energy diagram below, all levels are filled up to the
The
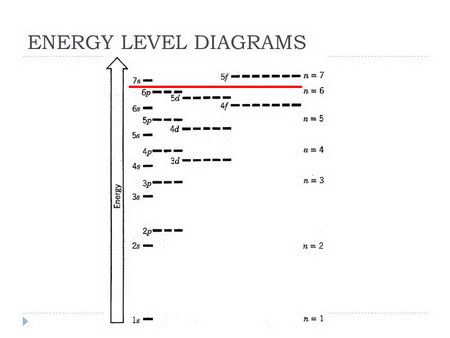
(Adapted from SlidePlayer)
A
Remember that
Removing these two electrons forms a
b. Paramagnetism
All electrons are paired in
The salts
A
Thus, elemental



