Question #3bb16
4 Answers
If you mean the last problem, the answer is 3) 3.92 m/s^2
Explanation:
Forces:
acting on two masses without friction
so
question 3 answer 1
Explanation:
Constant velocity means zero acceleration i.e. sum of forces is
or
Q no 11
Explanation:
Initial velocity of the car
Applied force
Final velocity of the car
Time taken to change in velocity
Acceleration produced
So by Newton's law the mass of the car
Q No 12
Explanation:
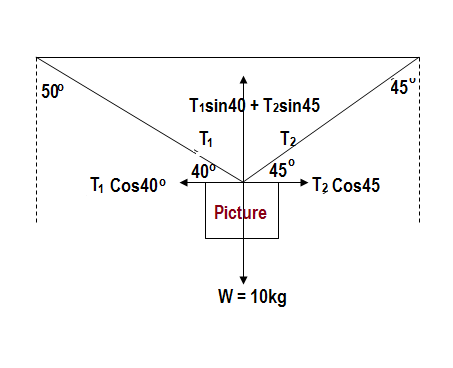
Considering the equilibrium of forces in the vertical horizontal direction we can write
Adding [1] and [2] we get


