How does the value of #sinx# change, as #x# increases from #pi/2# to #pi# radians?
1 Answer
Jan 22, 2018
As angle
Explanation:
The graph shown below depicts the changes in value is
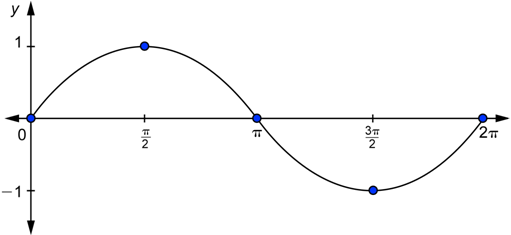
Observe that in
as
and again starts increasing from
Hence, as angle
