Question #4edaf
1 Answer
Refer to explanation
Respiration is a bit difficult to get your head around but it makes sense
Explanation:
We know the equation for aerobic respiration as:
Aerobic Respiration consists of Glycolysis, Link Reaction, Krebs' Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation.
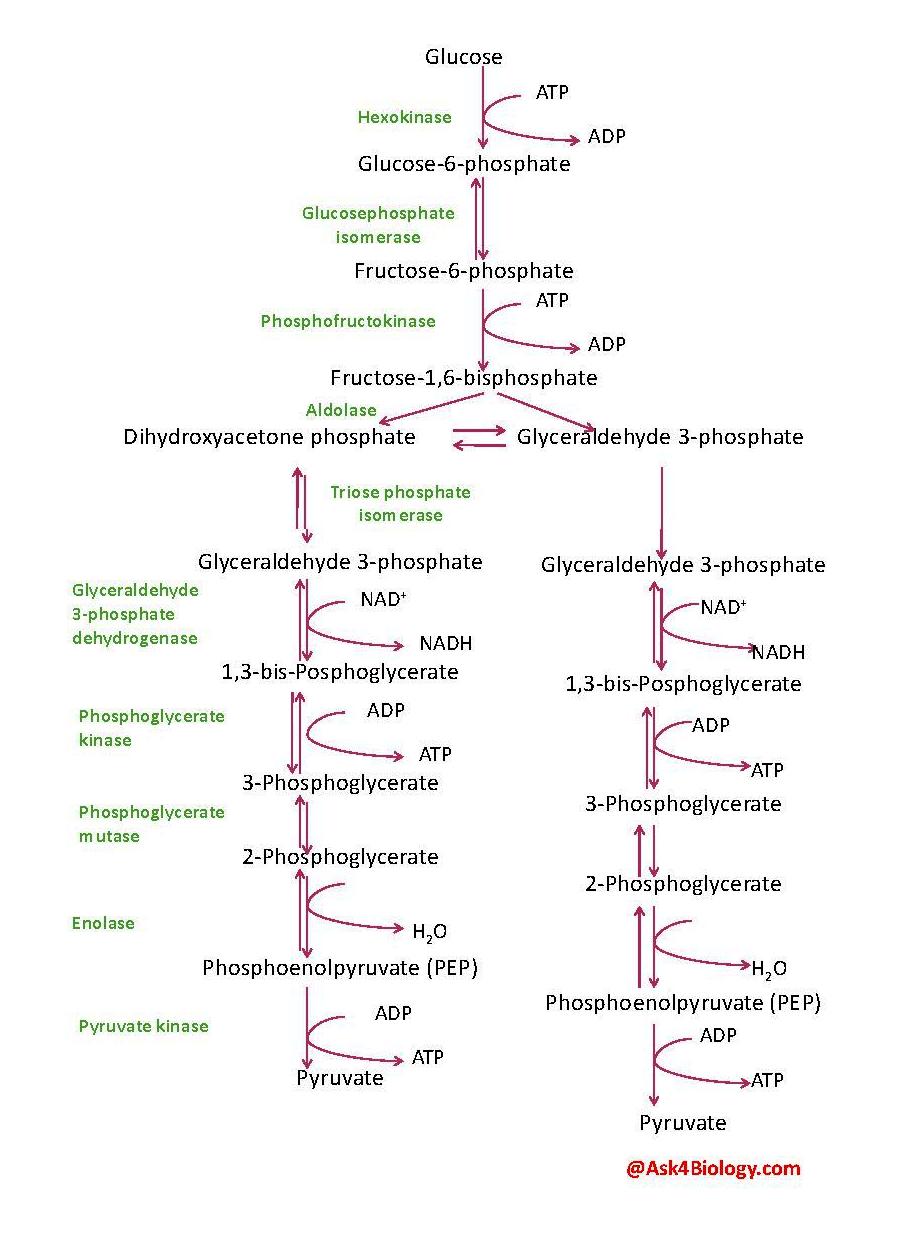
- Glycolysis: The aim of glycolysis to convert glucose to pyruvate(aka pyruvic acid). The image below shows the metabolic pathway of Glycolysis. The products of glycolysis are 2 molecules of pyruvate, 2 molecules of ATP, 2 molecules of NADH, 2 molecules of
#H_2O# ,#2H^+# and heat since it is an exothermic reaction.
Although 4ATP molecules are produced, 2ATP are used up at the beginning of the reaction so the overall ATP production in Glycolysis is 2ATP.
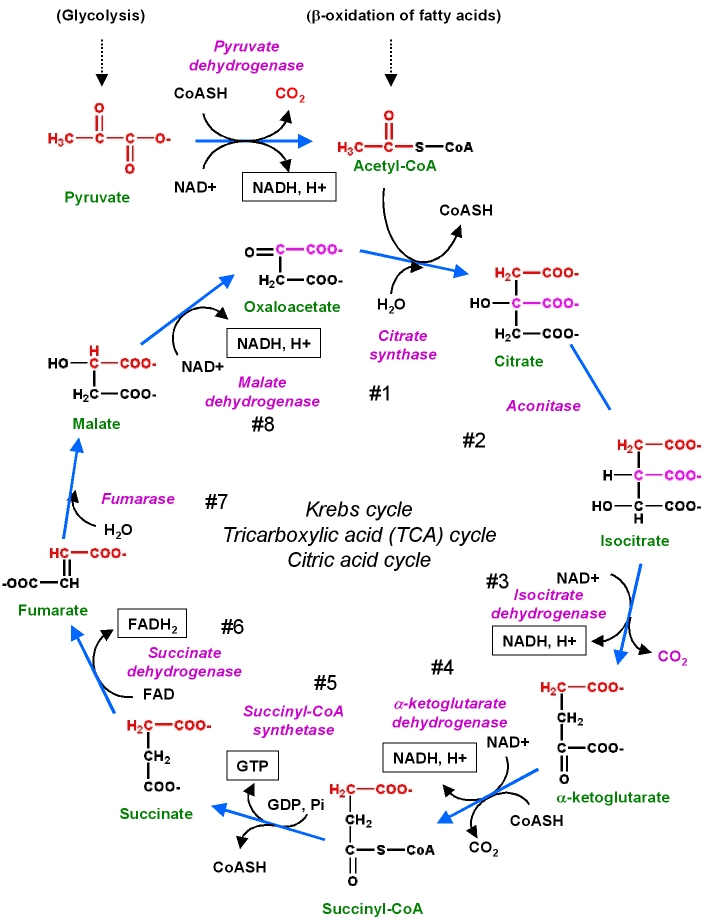
2: Link Reaction and Krebs' Cycle
The Link Reaction is at the beginning of Krebs' Cycle in which pyruvate is oxidatively decarboxylated where
In the Krebs' Cycle, in two cycles, 6NADH,
3: Oxidative Phosphorylation
The major yield of ATP comes from this reaction.
Click link below to learn about oxidative phosphorylation.
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
Watch video about calculation the ATP yield of aerobic respiration:
Calculating the ATP yield in cellular respiration
Anaerobic Respiration:
I will allow Mr Khan to explain because this answer would then be extremely long.
Bottom line is that the ATP yield for anaerobic respiration is

