What are the intermolecular forces?
1 Answer
Intermolecular forces:
- Van der Waals forces: ion-dipole, dipole-dipole, ion-induced dipole, dipole-induced dipole, London dispersion forces
- Hydrogen bond
See below for definitions and examples which can help you with the determination.
Explanation:
Ion-dipole interaction
If an ion and a polar molecule interact the result is an ion-dipole interaction.
On the picture below the positive ion
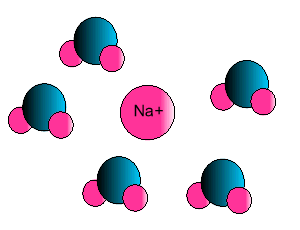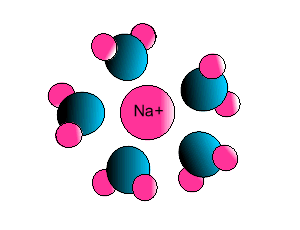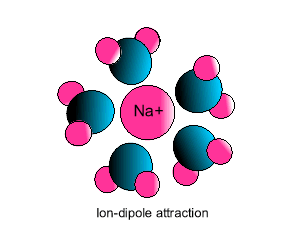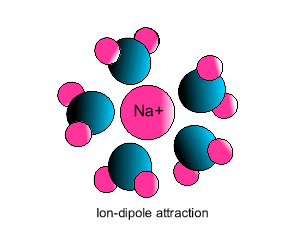
Hydrogen bonding
H-bonding is the interaction between an electronegative atom like oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine and a hydrogen atom.
On this gif below you can see interactions between
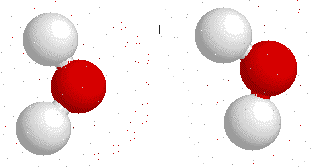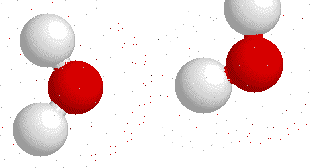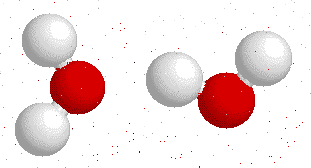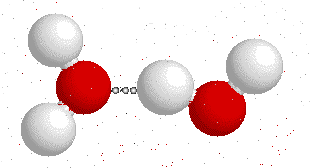
Hydrogen bonds also appear bewtween
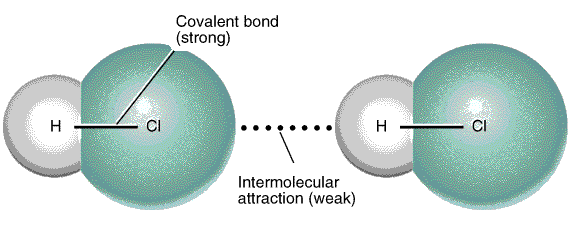
Dipole-dipole interaction
Dipole-dipole interactions are electrostatic interactions between molecules which have permanent dipole. The positive end of a polar molecule will attract the negative end of the other polar molecule. An example of this interaction is the intermolecular interaction between two
Ion-induced dipole interaction
Interactiton between an ion and a non-polar molecule. As you can see below the charge of the ion causes distortion of the electron cloud on the non-polar molecule. So we have an non-polar molecule in iteracttion with an ion and this ion produces a induced dipole/ polar molecule from a non-polar molecule.

revision=1
On the picture below there is an example of such interaction. We have a

Dipole-induced dipole interaction
A non-polar molecule turns into a induced dipole when it interacts with a polar molecule.

As a example we can take the interaction between the non-polar molecule

London dispersion forces/ induced dipole- induced dipole interaction
London forces are interactions between non-polar molecules. There is an instantaneous dipole moment caused by the movement of the electrons that causes such interaction.
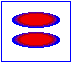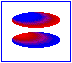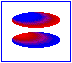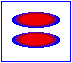
In the

A brief summary of my answer:


