How do you find the definite integral of #int (x^2-2)/(x+1)# from #[0,2]#?
1 Answer
Explanation:
Start by dividing the numerator by the denominator using long or synthetic division.
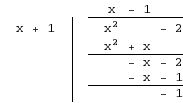
Thus:
We can integrate using the rules
Evaluate using
In celebration of this being the 2000th answer I ever wrote for socratic, I've included a whole bunch of practice exercises for your improvement
Practice exercises
- Evaluate each definite integral. Round answers to the nearest integer.
a)
b)
c)
Bonus
Hint: Use substitution
b)
Hopefully this helps!
Answers to practice exercises:
bonus:


