How do you find the missing length of an isosceles triangle given Base = 8 Angle = 30?
1 Answer
Jun 16, 2015
The length of the non-base sides is
Explanation:
(see diagram)
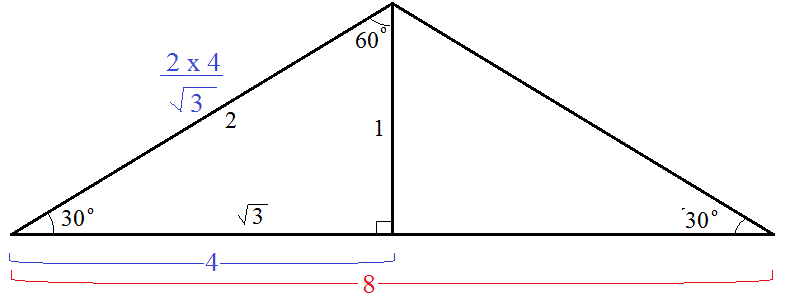
If the isosceles triangle is divided into two right-angled triangles, each resulting right-angled triangle has sides with well known proportions,
where the
the
Since "half isosceles base"
missing length
