How does molecular weight effect glass transition temperature?
1 Answer
The glass transition temperature
Explanation:
The glass transition temperature is the temperature range in which a polymer changes from a rigid “glassy” state to a more pliable “rubbery” state.
In polymer chemistry, the Flory–Fox equation relates the number-average molecular mass
#color(blue)(|bar(ul(color(white)(a/a) T_g = T_(g,∞) -K/M_n color(white)(a/a)|)))" "#
where
# T_(g,∞)# is the maximum value of#T_g# that can be achieved at a theoretical infinite molecular mass#K# is an empirical parameter that is related to the free volume present in the polymer sample.
The free volume is a measure of the room a polymer chain has in which to move in relation to the other polymer chains around it.
A polymer with long chains (high molecular mass) has less free volume than one with short chains.
Thus, low molecular mass gives lower values of
We see this behaviour in a typical Flory-Fox plot:
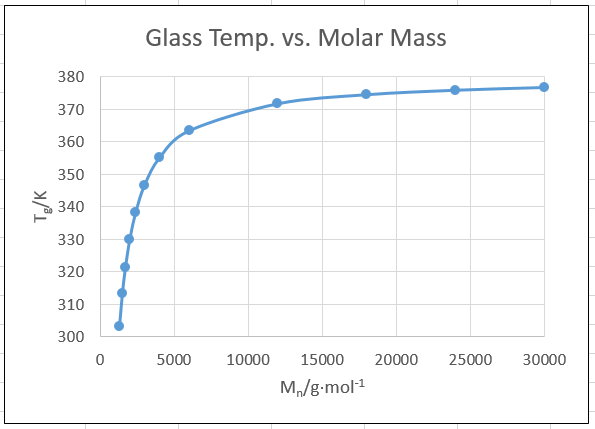
In the above plot,

