How will temperature affect the spontaneity of a reaction with positive #DeltaH# and #DeltaS#?
1 Answer
Spontaneous only at high temperatures.
Explanation:
At constant Temperature, and constant pressure, the change Gibbs free energy is defined as:
If the change in Gibbs free energy is negative, then the reaction will be spontaneous.
Finding the possible outcomes of different signs of
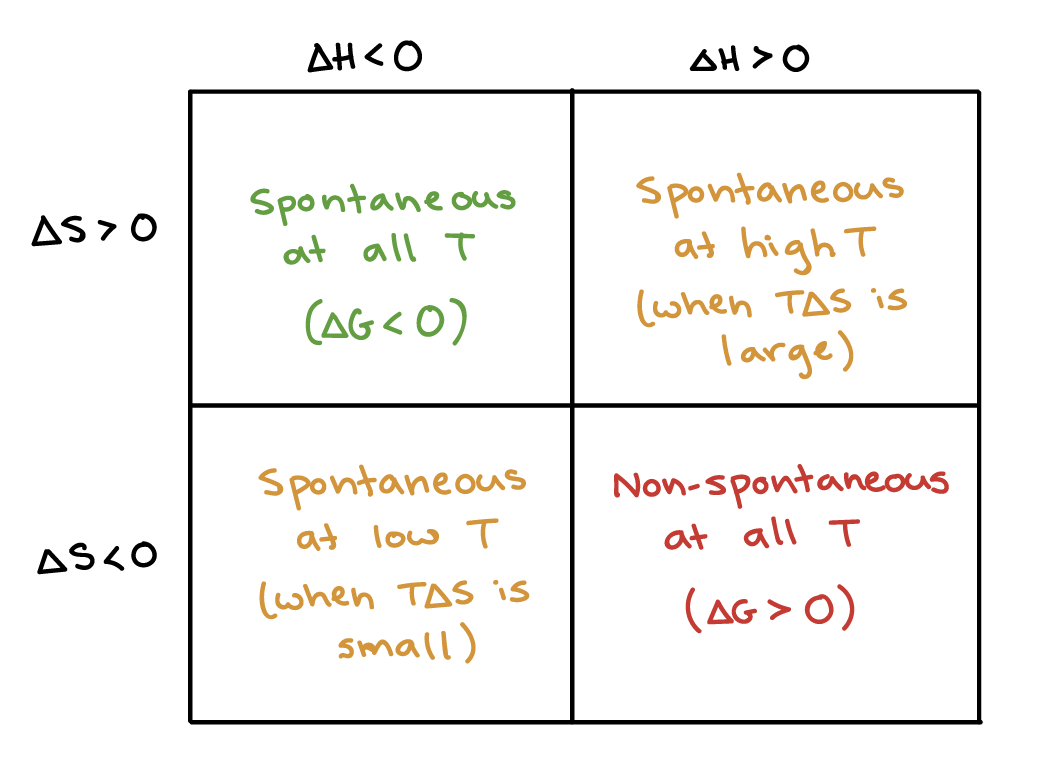
When
Since we suppose

