The graph below shows the height of a tunnel f(x), in feet, depending on the distance from one side of the tunnel x, in feet ?
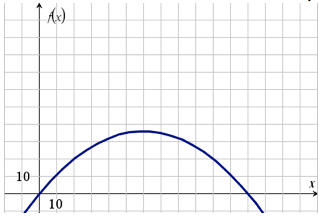
Part A: What do the x-intercepts and maximum value of the graph represent? What are the intervals where the function is increasing and decreasing, and what do they represent about the distance and height? (6 points)
Part B: What is an approximate average rate of change of the graph from x = 20 to x = 35, and what does this rate represent? (4 points)

Part A: What do the x-intercepts and maximum value of the graph represent? What are the intervals where the function is increasing and decreasing, and what do they represent about the distance and height? (6 points)
Part B: What is an approximate average rate of change of the graph from x = 20 to x = 35, and what does this rate represent? (4 points)
1 Answer
See below:
Explanation:
Part A
The x-intercepts, where the
The maximum
The interval where the function is increasing is
Part B
When
The approximate rate of change is then
or
This means that from 20 feet from the left of the tunnel to roughly 35 from the left of the tunnel, that for every 3 feet you move across the floor of the tunnel, the height of the tunnel rises 2 feet.
Another way to say this is that it is the slope of the roof of the tunnel at that point in the tunnel.

