Two masses, m1 =1.9kg and m2= 1.4kg, are attached by a string passing over a pulley as shown in the diagram below. The angle of inclination is theta= 25 degrees. The system is set in motion, and the masses travel a distance h= 1.3m at a constant speed?
What is the heat (delta H) generated by friction?
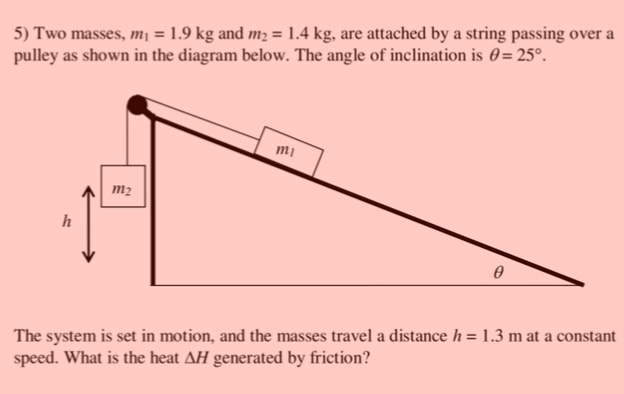
What is the heat (delta H) generated by friction?

1 Answer
By the condition of the problem the system is set in motion such that masses travel a distance h= 1.3m at a constant speed. We are to calculate the amount of heat generated during this motion.
So we can assume that during its motion no net force acts on the system and the constant speed gained by the system is due to the application of energy on the sytem from outside to initiate its motion.
So during this motion of connected system the loss of PE of
When
Here net loss in PE of the system provides energy required to do work done against force of friction and is converted to heat energy
Hence

