What is mechanical energy?
1 Answer
Below
Explanation:
Mechanical Energy is the sum of your gravitational and kinetic energy of all its parts.
If no other forces but gravity is present, energy will not be transferred into or out of the system, meaning mechanical energy is conserved. However, this is extremely rare.
An example of mechanical energy present is a pendulum
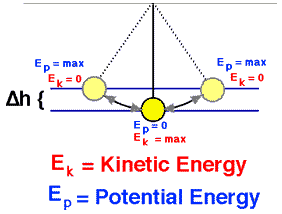
From the diagram, you can see that initially there is no kinetic energy but a lot of gravitational potential energy because the pendulum isn't moving and it is working against gravity, building potential. Remember, work is being put into the pendulum. Once the pendulum is released, kinetic energy builds up while the gravitational potential energy decreases at its "halfway" point. Similarly, once the pendulum reaches the other side, you can see once again that the kinetic energy is nought while gravitational potential energy is at its maximum.

