What is the boiling point (in °C) of a 1.56 m aqueous solution of CaCl_2?
1 Answer
The boiling point of the solution is
Explanation:
For this question we have to use the boiling point elevation equation:
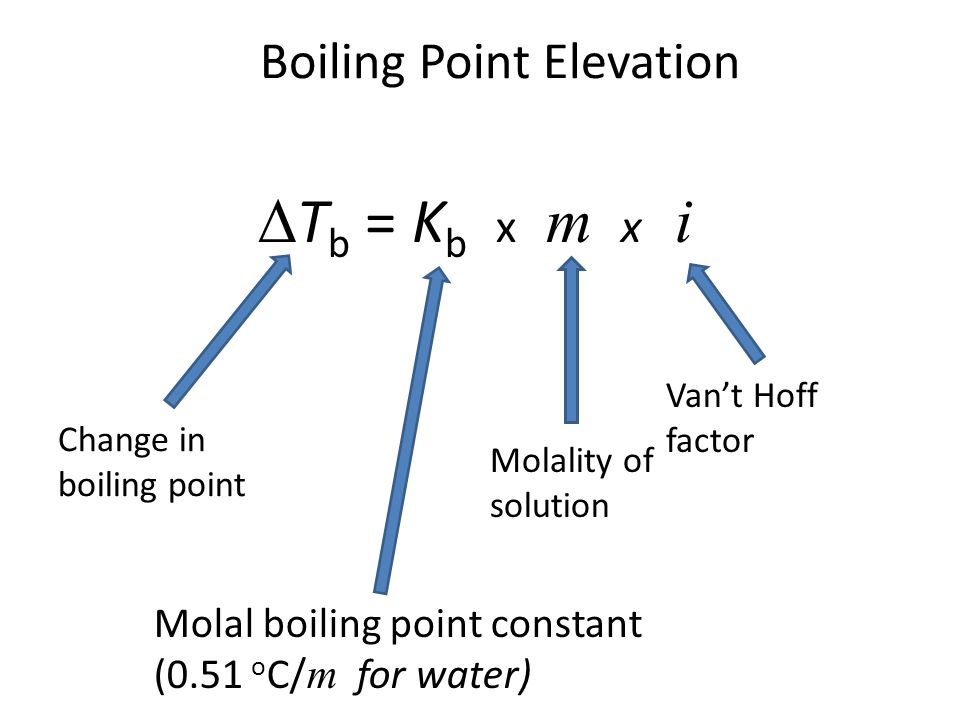 slideplayer.com
slideplayer.com
Now, let's determine our known and unknown variables:
Known:
molality
Van't Hoff factor
Molal boiling point constant (we're given this value)
Unknown:
Change in boiling point
I should mention that the Van't Hoff factor basically reflects the number of ions produced in solution upon dissociation of an ionic compound. The compound can also be a molecular one, but the Van't Hoff factor for that is just 1 because molecular compounds do not produce ions in solution.
When
You have one calcium ion and two chloride ions.
Now we can plug in what we know and solve for
Now, we add
***We added

