What is the electromagnetic spectrum? How is it used in astronomy?
1 Answer
The electromagnetic spectrum is the collection of all of the different wavelengths of light. In astronomy, the only information that we get from other stars and galaxies is in the form of light.
Explanation:
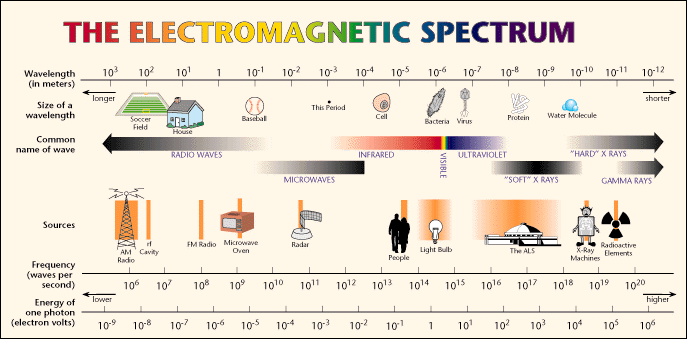 http://www2.lbl.gov/MicroWorlds/ALSTool/EMSpec/EMSpec2.html
http://www2.lbl.gov/MicroWorlds/ALSTool/EMSpec/EMSpec2.html
Electromagnetic radiation is generated by the motion of charged particles, such as electrons. All charged particles generate an electric field that permeates throughout space. When these particles move, they create a ripple in their electric field.
A magnetic field is then generated by the changing electric field, and a photon is generated. This is how electromagnetic radiation, or light, is generated.
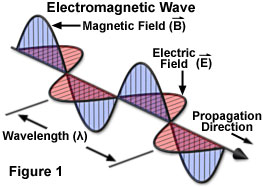 https://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/java/electromagnetic/index.html
https://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/java/electromagnetic/index.html
As the photon travels through space the electric and magnetic fields continue to oscillate at a constant rate. The rate of oscillation is called the frequency of the photon. Frequency is what determines the color of the light.
The collection of all of the colors of light is collectively referred to as the electromagnetic spectrum. In astronomy, light is the only information that we get from distant objects in space. Therefore, astronomers have developed a lot of different ways to investigate light. For instance, spectroscopy can tell us what a star is made of, and the brightest wavelength of light tells us the temperature of a star.

