What is the #+M# and #-M# effect? What are examples of electron releasing and electron withdrawing groups?
1 Answer
The mesomeric effect (or resonance effect) is the movement of π electrons toward or away from a substituent group.
Explanation:
For example, propenal has a mesomeric contributor in which the π electrons move towards the oxygen atom.
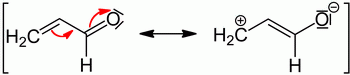
(from en.wikipedia.org)
The molecule therefore has a
Since the electrons have moved away from the rest of the molecule and towards the
Other
If the π electrons move away from the group and towards the rest of the molecule, the effect is called a
An example is the donation of electrons from an amino group into a benzene ring, putting

Other

