What is an ambident nucleophile?
1 Answer
An ambident nucleophile is an anionic nucleophile in which the negative charge is delocalized over two unlike atoms.
Explanation:
A nucleophile is a chemical species that can donate an electron pair and form a bond to a carbon atom. For example,

The word ambident comes from two Latin words: ambi = "on both sides" + dens = "tooth".
So an ambident nucleophile has "teeth" on two sides.
It can attack from two different places and form two different products.
For example, the thiocyanate ion,
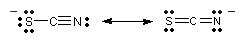
Both the
So, the
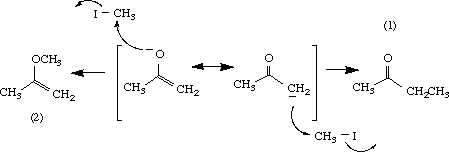
A common ambident nucleophile in organic chemistry is the enolate ion.
For example, the resonance forms of acetone enolate are
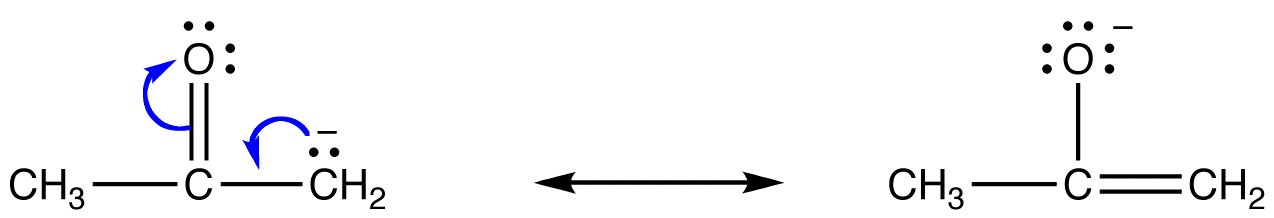
Both the
Thus, the reaction of the enolate with methyl iodide gives a mixture of a ketone (1) and an enol ether (2).