What is the role of ATP and ADP in cellular respiration?
1 Answer
ATP is consumed in glycolysis to convert glucose to pyruvate, and produced in electron transport chain.
Explanation:
Cellular respiration consists of three parts in order: glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain.
Glycolysis involves total of 10 steps. Out of those, step 1 and 3 use ATP.
 upload.wikimedia.org
upload.wikimedia.org
-
In step 1, hexokinase (HK) take a phosphate from ATP and add the phosphate to glucose to create glucose-6-phosphate. Because a phosphate is taken out, ATP becomes ADP.
-
In step 3, phosphofructokinase (PFK) take a phosphate from ATP and add the phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate to create fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
 www.wiley.com
www.wiley.com
Electron transport chain consists of many steps as well. Out of those, the last step produces ATP.
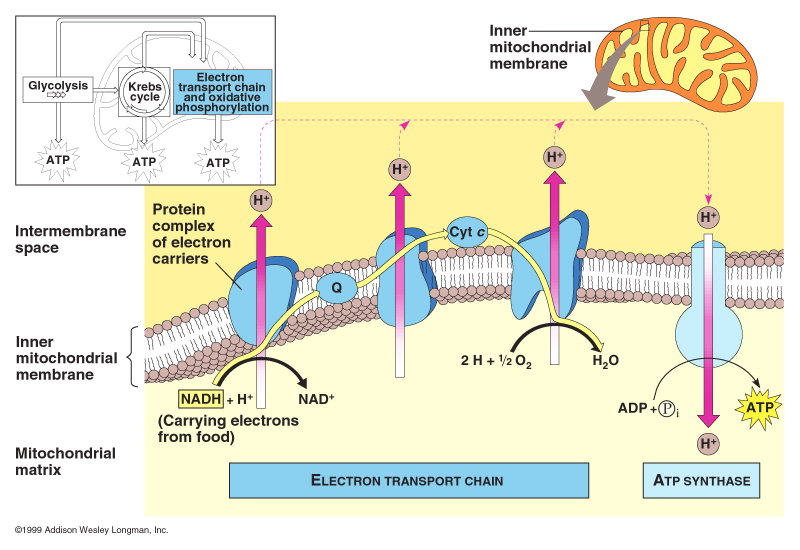
In last step, ATP synthase uses the difference in hydrogen ion concentration to make ATP.
- NADH catalyzes a series of reactions with several proteins to move hydrogen cations from mitochondrial matrix to intermembrane space. This creates a difference in hydrogen cation concentration.
- The higher concentration in intermembrane space means hydrogen cations prefer to go back to mitochondrial matrix.
- ATP synthase use this force to drive reaction that adds a phosphate to ADP to create ATP.
More about phosphofructokinase (PFK)
More about electron transport chain

