In a polynomial fraction #f(x) = (p_n(x))/(p_m(x))# we have:
#1)# vertical asymptotes for #x_v# such that #p_m(x_v)=0#
#2)# horizontal asymptotes when #n le m#
#3)# slant asymptotes when #n = m + 1#
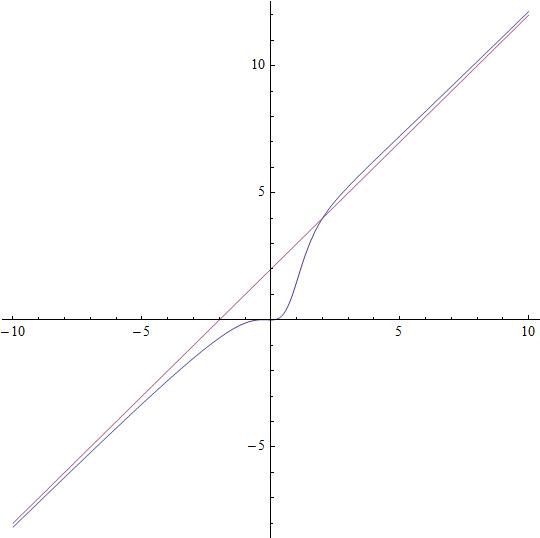
In the present case we dont have vertical asymptotes and #n = m+1# with #n = 3# and #m = 2#
Slant asymptotes are obtained considering #(p_n(x))/(p_{n-1}(x))
approx y = a x+b# for large values of #abs(x)#
In the present case we have
#(p_3(x))/(p_2(x)) = ( 2x^3 + x^2)/ (2x^2 - 3x + 3)#
#p_3(x)=p_2(x)(a x+b)+r_1(x)#
#r_1(x)=c x + d#
# 2x^3 + x^2 = (2x^2 - 3x + 3)(a x + b) + c x + d#
equating coefficients
#{
(-3 b - d=0), (-3 a + 3 b - c=0), (1 + 3 a - 2 b=0), (2 - 2 a=0)
:}#
solving for #a,b,c,d# we have #{a = 1, b = 2, c = 3, d = -6}#
substituting in #y = a x + b#
#y = x +2#
Note that
#(p_3(x))/(p_2(x))=(a x+b)+(r_1(x))/(p_2(x))#
and as #abs(x) # increases #(r_1(x))/(p_2(x))->0#